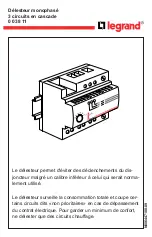
BE1-51C Functional Description
3-3
Loss-of-Power Sensing
A loss-of-power circuit monitors the power supply. If power is interrupted, the Relay Disabled output contact
closes as explained later in this section (under Outputs).
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL (A/D) CONVERTER
The voltage representing the sensed current is applied to the A/D converter. The A/D converter supplies
the equivalent binary value of the sensed current to the trip comparator. The trip comparator stores a
number of these samples, and calculates the true RMS value of the current at each input.
INTERNAL MICROCOMPUTER
The onboard computer fulfills many of the logic and signal processing functions described in the following
paragraphs, and performs the time delay computations.
Time Overcurrent Calculations
If the magnitude of the current exceeds the pickup setting, the microprocessor calculates the required time
delay by evaluating the magnitude of the overcurrent in the context of the selected time overcurrent
response curve. (All of the time overcurrent functions that are graphically illustrated in Figures 1-2 through
1-8 are in the computer memory.) The data inputs are continuously polled and the calculations updated
once for every 60 Hz (line) cycle.
As long as the sensed current is above the pickup point, the elapsed time is accumulated toward trip. Once
the sensed current falls below pickup, the relay is reset and all accumulated time is cancelled.
When the value of a sensed current exceeds the pickup setting, the TIMING LED for that phase lites and
indicates timing has started. The LED stays lit after the output relay has tripped for as long as the sensed
current exceeds the selected pickup level.
High/Low Range Register
It was noted earlier in this section that the input transformers must be wired for one of two sensing ranges:
HIGH or LOW. This information is recorded (at the factory) into the HI/LO Range Registers
one register
for the phases, one for neutral. All current sensing and pickup data is weighted by the computer accordingly.
Watchdog Circuitry
The watchdog circuit checks that the microcomputer is operational. If some transient condition has disrupted
its normal pattern of operation, the watchdog will momentarily close the Relay Disabled output contact, reset
the computer, and initialize the program. The microcomputer is then automatically restarted, and the relay
resumes its monitoring function (without human input). A SCADA program can be devised to record the date
and time of the event.
OUTPUTS
General
Although the output relays are controlled by the microcomputer, the output interface contains the transistors
that energize them. With the exception of the Relay Disabled contact (described below), all of the output
contacts are of the normally open type and have targets associated with them.
Relay Disabled Output
Summary of Contents for BE1-51C
Page 12: ...BE1 51C General Information 1 6 Figure 1 1 Style Number Identification Chart...
Page 21: ...BE1 51C Controls and Indicators 2 2 Figure 2 1 Location of Controls and Indicators...
Page 25: ...BE1 51C Functional Description 3 2 Figure 3 1 Functional Block Diagram...
Page 49: ...BE1 51C Operation By Computer 5 14 Figure 5 1 RS 232 Port Connector Wiring...
Page 50: ...BE1 51C Operation By Computer 5 15 Figure 5 2 RS 485 Port Connector Wiring...
Page 58: ...BE1 51C Installation and Testing 6 8 Figure 6 1 Outline Dimensions...
Page 62: ...BE1 51C Installation and Testing 6 12 Figure 6 8 Relay Connections...