11
3.5.3 WLAN Settings
Referring to You can
enable/disable an SSID from this page.
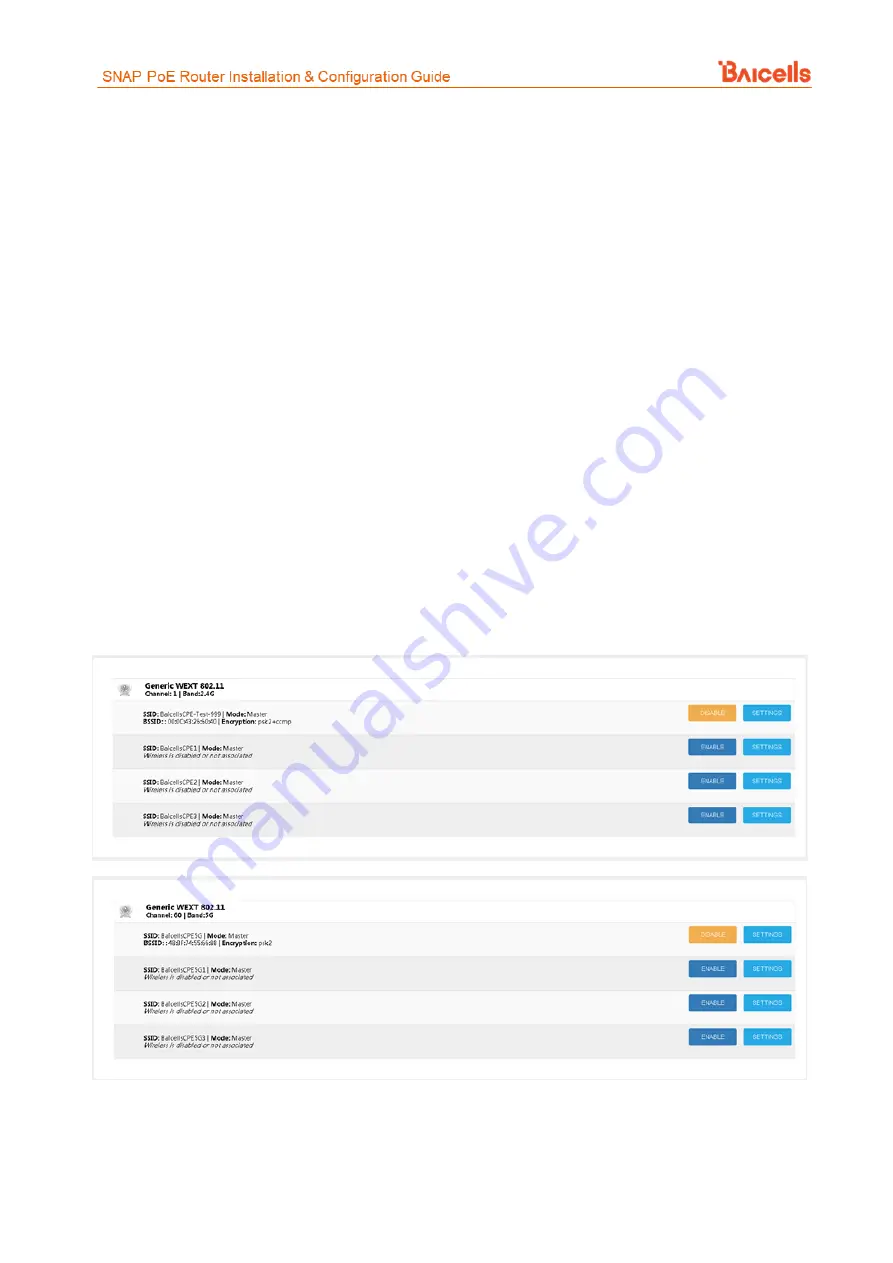
, this window displays the Wireless LAN (WLAN) status, including the:
•
Channel being used in which band, e.g., 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz
•
Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs) enabled and disabled.
−
When you set up a Small Office or Home Office (SOHO) wireless network, you give it a name
to distinguish it from other WLANs in your neighborhood whose wireless signals you are
able to receive on your device(s).
−
Some SOHO WLANs have more than one SSID, e.g., one for 2.4 GHz and one for 5 GHz. Why?
Since not all end-user devices support 5 GHz, using the 5 GHz SSID might be less congested
and provide better service.
−
SSIDs also provide a way to segment the WLAN for users with different security and VLAN
configurations.
−
SNAP PoE Router model EP3011 supports up to 8 SSIDs, 4 for 2.4 GHz and 4 for 5.8 GHz.
•
Mode - Master or Client, where Master changes the device's channel to match its channel
•
Basic Service Set Identifiers (BSSID) - the MAC addresses of Wireless Access Points (WAP)
•
Encryption method - security protocol being used
You can enable/disable an SSID from this page.
Figure 13: WLAN (1 of 2)
At the bottom of the WLAN window is a list of any devices associated with each SSID (
Figure 14). The information includes the MAC address, IP address, signal strength (dBm), and current data
rate. The data rate includes the speed (Mbps), the Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS) value - an indication
of signal quality, and the channel bandwidth (MHz).















































