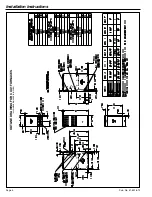
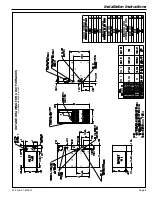
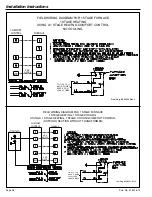
Installation Instructions
Page 13
Pub. No. 41-5016-12
NOTE:
It is recommended that the first joints from the furnace be
connected and sealed with high temperature RTV. This will
enable the pipes to be removed later without cutting.
Be sure to properly support these joints.
BONDING OF PVC
Commercially available solvent cement must be used to join the
pipe and fittings. Follow instructions on the container carefully.
Procedure for Cementing Joints:
1. Cut pipe square, remove ragged edges and burrs. Chamfer end
of pipe, then clean fitting socket and pipe joint area of all dirt,
grease, moisture or chips.
2. After checking pipe and socket for proper fit, wipe socket and
pipe with cleaner-primer. Apply a liberal coat of primer to inside
surface of socket and outside of pipe.
DO NOT ALLOW PRIMER TO DRY BEFORE APPLYING
CEMENT.
3. Apply a thin coat of cement evenly in the socket. Quickly apply
a heavy coat of cement to the pipe end and insert pipe into fitting
with a slight twisting movement until it bottoms out.
4. Hold the pipe in the fitting for 30 seconds to prevent tapered
socket from pushing the pipe out of the fitting.
5. Wipe all excess cement from the joint with a rag. Allow 15
minutes before handling. Cure time varies according to fit, tem-
perature and humidity.
NOTE:
Follow venting instructions carefully when using PVC cement.
IMPORTANT:
All joints must be water tight. Flue condensate is somewhat acidic,
and leaks can cause equipment damage.
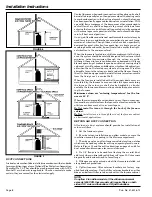
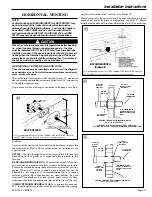
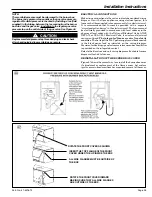
Connection of the pipe and collar of the
combustion air inlet
should just be a friction fit. It is recommended that the inlet air
joint be sealed with RTV type sealant to allow the joint to be
separated for possible future service. The inlet and vent pipes
must be properly supported throughout the entire length.
Connection of the
vent pipe
to the vent collar should also be
accomplished using RTV type sealant. This type sealant provides
a connection which remains flexible and can be separated in the
future if service needs require the removal of the vent pipe for
service or clearance.
NOTE:
To ensure proper operation at the vent lengths indicated, the
combustion air inlet and vent terminals should be in the same
pressure zone. Terminating the vent and inlet in different
pressure zones will change the maximum vent lengths and
may cause nuisance tripping of the pressure switch(es). The
amount of change can not be predicted. The selection of the
inlet and outlet terminal locations are the responsibility of the
designer/installer. If the installer chooses separate pressure
zones for the terminals, the combustion air inlet termination
must be in the higher (more positive) pressure zone.
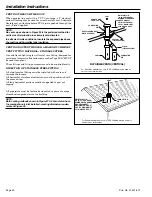
Seal
VENT PIPE
with RTV sealant
Seal
INLET AIR PIPE
with RTV sealant
Front of Furnace
VENT AND INLET AIR CONNECTIONS
f
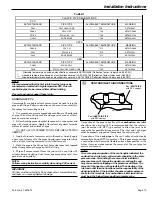
TABLE 7
PLASTIC PIPE DESIGNATIONS
PVC
ASTM STANDARD
PIPE TYPE
ALLOWABLE TEMPERATURE
MARKING
F891
CELLULAR CORE
*158
ASTM F891
D2665
DWV PIPE
**158
ASTM D2665
D1785
SCH 40, 80, 120
**158
ASTM D1785
D2241
SDR SERIES
**158
ASTM D2241
CPVC
ASTM STANDARD
PIPE TYPE
ALLOWABLE TEMPERATURE
MARKING
D2846
CPVC 41
**212
ASTM D2846
F441
SCH 40, 80
**212
ASTM F441
F442
SDR SERIES
**212
ASTM F442
ABS
ASTM STANDARD
PIPE TYPE
ALLOWABLE TEMPERATURE
MARKING
D2661
SCH 40 DWV
***180
ASTM D2661
F628
SCH 40 DWV CELLULAR CORE
***180
ASTM F628
* - Allowable temperatures based on classifications covered in ASTM D4396 [Deflection Temps Under Load (264 PSI)]
** - Allowable temperatures based on classifications covered in ASTM D1784 [Deflection Temps Under Load (264 PSI)]
*** - Allowable temperatures based on classifications covered in ASTM D3965 [Deflection Temps Under Load (264 PSI)]