56
Agilent 86038B Photonic Dispersion and Loss Analyzer, Second Edition
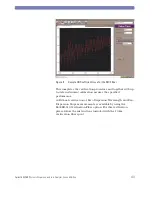
• When measuring DGD, any GD drift or disturbance of the
DUT GD during each measurement can bias the measurement
point to higher DGD. This effect might be seen as a single
measurement point spike if the DUT or fibers were bumped
during the measurement.
Note that DGD is far more sensitive to this than PDL.
Polarization Dependent Loss (PDL)
Polarization dependent loss (PDL) is the peak-to-peak variation
in the loss of a test device over all polarization states.
The mechanisms that produce PDL include material absorption,
oblique optical reflections, fiber bends and various aspects of
optical circuit design. In cases of passive components exhibiting
pure PDL (without significant PMD), the polarization states
corresponding to maximum and minimum loss are diametrically
opposite one another on the Poincare sphere.
Tips on Measuring Polarization Dependent Loss (PDL)
• Similar considerations as for DGD apply to making accurate
PDL measurements. In particular, noise and drift should be
minimized. Care should also be taken to avoid other sources
of PDL in the measurement setup, like switches with
appreciable PDL or noncontacted angled connectors.
Fiber length
This measurement may be applied to any test device, but is
usually applied to optical fiber. The fiber length is derived from
measurement of the derivative of RF modulation phase with RF
frequency, at a user-defined wavelength. The optical length
measurement uncertainty is below 10
-6
of the total length, for
fibre lengths
~
50km. The 50 km length limit applies to the
specification, but very accurate measurements can be made to
any practical length. The measurement determines optical
length, nL, so calculation of physical length requires the user to
enter the value of the index of refraction; any error in the index
of refraction directly impacts the length measurement.
Note also that the length also changes with temperature
significantly with respect to this accuracy level. A rough figure
for the temperature dependence of the optical length on
temperature for standard SMF is about 10
-5
/°C.
Summary of Contents for 86038B
Page 1: ...Agilent 86038B Photonic Dispersion and Loss Analyzer User s Guide ...
Page 4: ...4 ...
Page 20: ...20 Agilent 86038B Photonic Dispersion and Loss Analyzer Second Edition ...
Page 34: ...34 Agilent 86038B Photonic Dispersion and Loss Analyzer Second Edition Figure 2 b Rear Panel ...
Page 78: ...78 Agilent 86038B Photonic Dispersion and Loss Analyzer Second Edition ...
Page 92: ...92 Agilent 86038B Photonic Dispersion and Loss Analyzer Second Edition ...
Page 202: ...202 Agilent 86038B Photonic Dispersion and Loss Analyzer Second Edition End Sub ...
Page 348: ...348 Agilent 86038B Photonic Dispersion and Loss Analyzer Second Edition ...
Page 349: ......