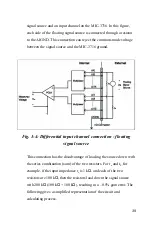
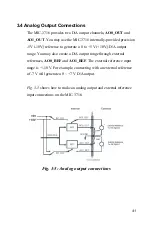
32
3. Signal Connections
3.1 Overview
Maintaining signal connections is one of the most important factors in
ensuring that your application system is sending and receiving data
correctly. A good signal connection can avoid unnecessary and costly
damage to your PC and other hardware devices. This chapter provides
useful information about how to connect input and output signals to
the MIC-3716 via the I/O connector.
3.2 I/O Connector
The I/O connector on the MIC-3716 is a 68-pin connector that enables
you to connect to accessories with the PCL-10168 shielded cable.
Note:
The PCL-10168 shielded cable is especially designed for the MIC-3716 to
reduce noise in the analog signal lines. Please refer to
1.4 Accessorie
s.
Pin Assignment
Fig. 3-1
shows the pin assignments for the 68-pin I/O connector on the
MIC-3716.
Note:
Summary of Contents for MIC-3716
Page 2: ...ii This page is left blank for hard printing...
Page 6: ...vi This page is left blank for hard printing...
Page 8: ...viii Table E 2 D A binary code table 117...
Page 11: ...1 Introduction 1 CHAPTER...
Page 17: ...7 Fig 1 1 Installation Flow Chart...
Page 21: ...11 Installation and Configuration CHAPTER 2...
Page 40: ...30 This page is left blank for hard printing...
Page 41: ...31 Signal Connections CHAPTER 3...
Page 44: ...34 Fig 3 1 I O connector pin assignments for the MIC 3716...
Page 50: ...40...
Page 54: ...44 This page is left blank for hard printing...
Page 55: ...45 Software Programming Overview CHAPTER 4...
Page 60: ...50 This page is left blank for hard printing...
Page 61: ...51 Calibration CHAPTER 5...
Page 77: ...67 Appendixes...
Page 81: ...71 Appendix B Block Diagrams...
Page 82: ...72 This page is left blank for hard printing...
Page 120: ...110 This page is left blank for hard printing...