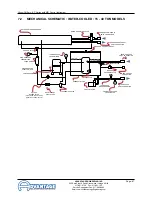
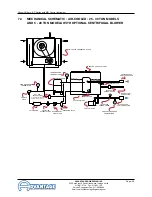
Glycol Chillers : BC Series with MG Control Instrument
Page: 62
ADVANTAGE ENGINEERING, INC.
525 East Stop 18 Road Greenwood, Indiana 46142
317-887-0729 Fax: 317-881-1277
Service Department Fax: 317-885-8683
Email: [email protected]
6.1 WATER SYSTEM
A.
MOTOR/PUMP ASSEMBLY: The motor/pump
assembly circulates chilled fluid to the process loop.
The pump assembly is built of total stainless steel to
maintain water quality.
B.
RESERVOIR. The vented reservoir is sized for the
chiller application to support the flow rate. The reservoir
provides a stable water temperature under varying load
conditions.
6.2 REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
A.
COMPRESSOR: Compressors take low pressure/low
temperature refrigerant gas and compress the gas into
high pressure/high temperature gas.
B.
AIR COOLED CONDENSER: The air cooled
condenser removes heat from the compressed
refrigerant gas. The action causes the gas to
“condense” into a liquid state still under high pressure.
Air flow across the condenser is achieved via a motor
driven fan assembly or centrifugal blower.
C.
WATER COOLED CONDENSER: The water cooled
condenser removes heat from the compressed
refrigerant gas. As the heat is removed, the gas
“condenses” into a liquid state, still under high
pressure. Water regulator valves are used on all
models to control the refrigerant head pressure by
modulating the condenser water flow.
D.
FILTER-DRIER: The filter-drier removes contaminants
and moisture from the liquid refrigerant.
E.
REFRIGERANT SIGHT GLASS: The refrigerant
sight glass indicates refrigerant charge and moisture
content.
• Full refrigerant charge is determined by a
clear liquid flow.
• Bubbles indicate low refrigerant.
• Moisture content is indicated by the color of
the element.
• Element color is normally green.
Typical Filter Drier
Typical Air-Cooled Condenser
Reservoir
Compressor
Coolant Pump
Typical Water-Cooled Condenser