42
Operation Theory
HSL_M_start_ta_move_zu()
HSL_M_start_sr_move_xy()
HSL_M_start_sr_move_zu()
HSL_M_start_sa_move_xy()
HSL_M_start_sa_move_zu()
The second group allows user to freely assign the 2 target axes.
HSL_M_start_tr_line2()
HSL_M_start_sr_line2()
HSL_M_start_ta_line2()
HSL_M_start_sa_line2()
The characters “t”, “s”, “r”, and “a” after HSL_M_start mean:
X
t – Trapezoidal profile
X
s – S-Curve profile
X
r – Relative motion
X
a – Absolute motion
3-Axis Linear Interpolation
Any 3 of the 4 axes of the HSL-4XMO may perform 3-axis linear
interpolation. As shown the figure below, 3-axis linear interpolation
means to move the XYZ (if axes 0, 1, 2 are selected and assigned
to be X, Y, Z respectively) position from P0 to P1, starting and
stopping simultaneously. The path is a straight line in space.
Figure 4-12: 3-Axis Linear Interpolation
Summary of Contents for HSL-4XMO
Page 4: ......
Page 16: ...6 Introduction ...
Page 36: ...26 Signal Connections ...
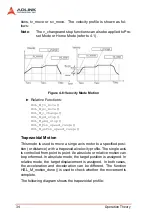
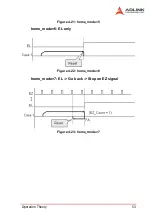
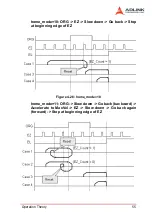
Page 67: ...Operation Theory 57 Home Search Example Home mode 1 Figure 4 29 Home Search Example ...
Page 108: ...98 Motion Creator in LinkMaster ...