SOTOX A™ MOBILE ANALY ZER | USER GUIDE
28 | EN
10. SUPERVISOR M AIN MENU
10.1.4 Exporting diagnostics data
Diagnostics data can be exported from the SoToxa™ Mobile Analyzer to an SD card, if required and instructed to by Customer Service on behalf of the
manufacturer. This data can be used to aid with troubleshooting of a particular issue or as part of routine monitoring of how the system is working.
To export the diagnostics data to an SD card, follow these steps.
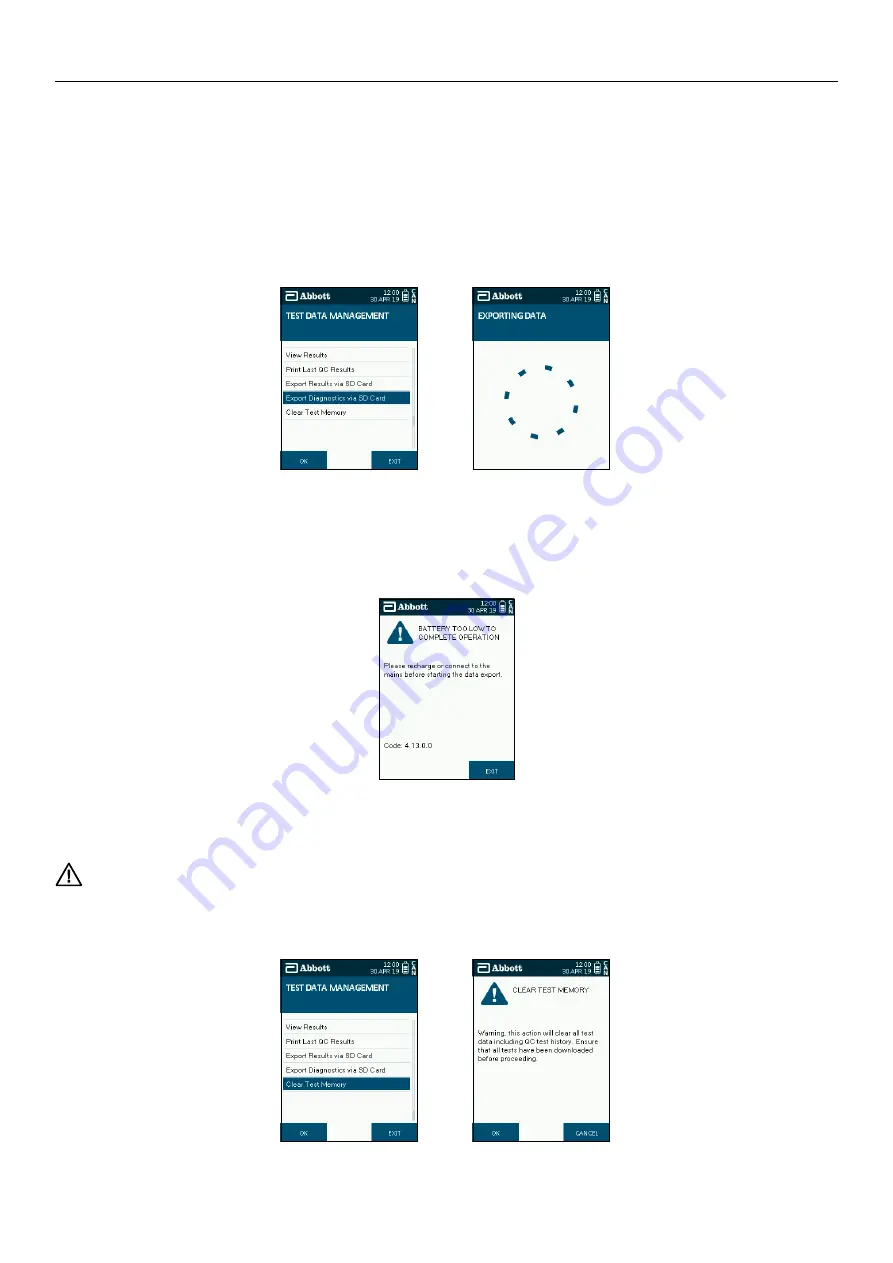
Step 1: Insert the SD card into the analyzer before starting this procedure.
Step 2: From the Test Data Management menu, select the Export Diagnostics via SD Card option.
Step 3: A progress wheel will be displayed while the data is being exported. It may take several minutes to complete as it is dependent on the number
of tests completed on the analyzer.
Step 4: On completion of the export the main menu will be displayed.
Step 5: Turn the analyzer off and remove the SD card from the slot and return to Customer Service as instructed.
Step 6: Re-screw the card cover into place.
Please note that if the battery is too low, then the warning message shown below will appear when you start to export the data. Either charge the
analyzer or simply connect to the mains before starting the export again.
10.1.5 Clear test memory
The test memory of the SoToxa™ Mobile Analyzer can be cleared following data export as described in section 10.1.3 Exporting results or when
the when storage capacity is reached on the analyzer.
This action will clear all the test data including the QC test history which means the user will be locked out of completing any further
subject tests until a successful QC check has been completed. See section 8.4 QC lockout for further information.
Step 1: To clear the test memory, from the Test Data Management menu, select the Clear Test Memory option.
Step 2: A warning screen will be shown to the user, to acknowledge select OK to continue with clearing the memory or cancel to return to the Test
Data Management menu and export results as previously described.
Step 2
Step 3
Step 1
Step 2


























