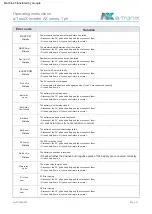
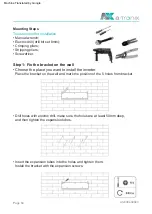
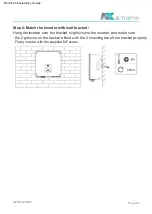
atx009en0823
Page 52
the installation.
Avoid temporary repairs.
• All repairs should be carried out using only approved spare parts, which must be
installed in accordance with their intended use and by a licensed contractor or
authorized service representative. •
Liabilities arising from commercial components are delegated to their
respective manufacturers. •
Any time the inverter has been disconnected from the public network, please be
extremely cautious as some components can retain charge sufficient to create a
shock hazard. Prior to touching any part of the inverter please ensure surfaces and
equipment are under touch safe temperatures and voltage potentials before
proceeding.
• Do not use the equipment when the safety devices do not work or are disabled. •
Use personal protective equipment, including gloves and eye protection during
• Do not use the equipment if any operating anomalies are found.
energized cable comes into contact with a grounded person, an additional current
flows, known as a residual current.
• Inform the manufacturer about non-standard installation conditions.
PV System Residual Current Factors • In
every PV installation, several elements contribute to the current leakage to protective
earth (PE). these elements can be divided into two main types. • Capacitive
discharge current - Discharge current is generated mainly by the parasitic
capacitance of the PV modules to PE. The module type, the environmental
conditions (rain, humidity) and even the distance of the modules from the
roof can effect the discharge current. Other factors that may contribute to the parasitic
capacitance are the inverter's internal capacitance to PE and external protection
elements such as lighting protection. • During operation, the DC bus is
connected to the alternating current grid via the inverter. Thus, a portion of the
alternating voltage amplitude arrives at the DC bus. The fluctuating voltage
constantly changes the charge state of the parasitic PV capacitor (ie capacitance
to PE). This is associated with a displacement current, which is proportional to
the capacitance and the applied voltage amplitude.
• Residual current - if there is a fault, such as defective insulation, where an
2.2 PE Connection and Leakage Current
Machine Translated by Google