2N TELEKOMUNIKACE a.s., www.2n.cz
29/143
2.4 IP Voice Transmission
Speech Encoding Methods
Voice transmission is strictly separated from signalling in VoIP networks. Modern VoIP
networks mostly use the RTP (Realtime Transport Protocol) for voice transmission.
The purpose of the RTP is only to transmit data (voice) from a source to a destination
at real time. Codecs are used to save the channel data capacity. Codecs process the
voice signal using variable algorithms to minimise the volume of user data. The degree
of compression used by the codec affects the quality of voice transmission. Thus, the
better voice transmission is required, the wider data range (the higher transmission
rate) is needed. The MOS (Mean Opinion Score) scale is used for rating voice
transmission quality, where 1 means the worst and 5 the best quality. For a survey of
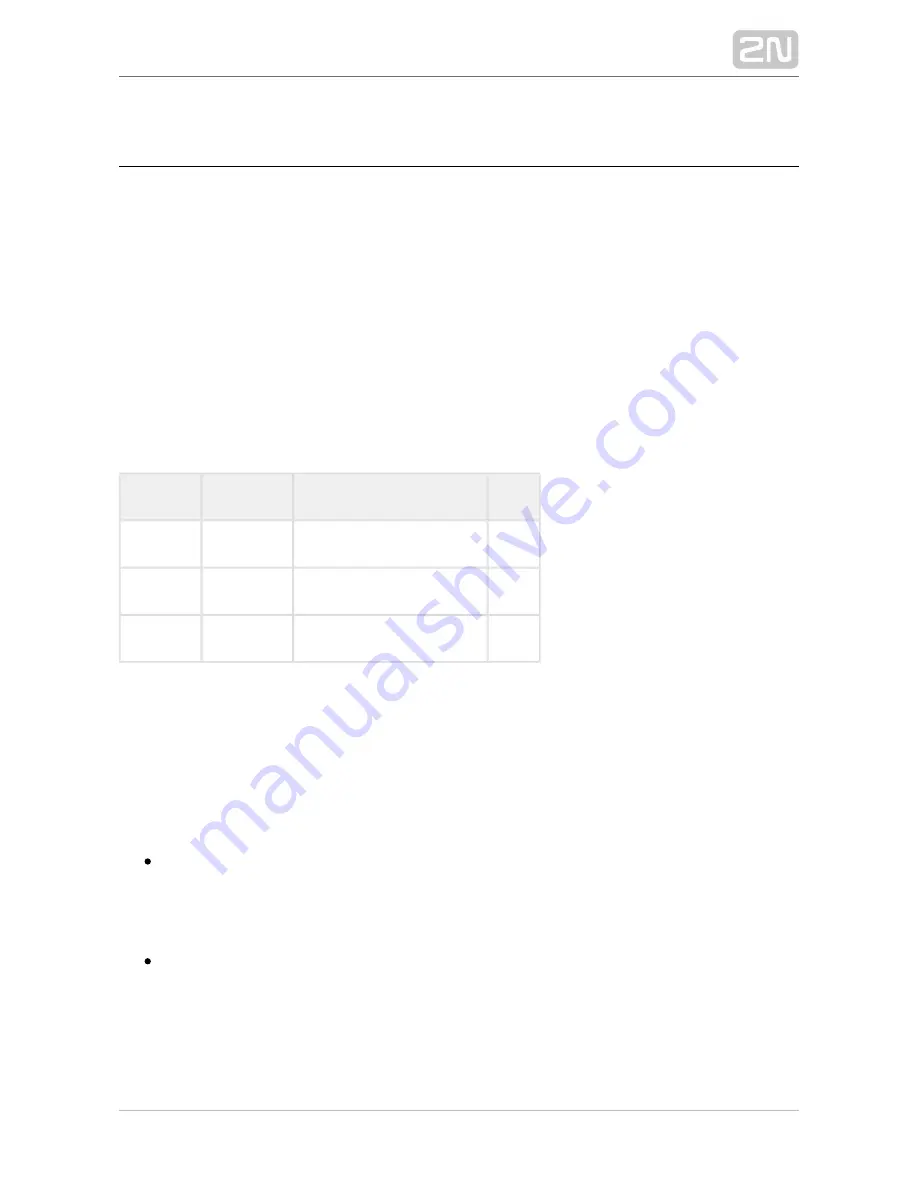
the codecs supported by
refer to the table below.
2N VoiceBlue MAX
®
Standard
Algorithm
Transmission rate [kbps]
MOS
G.711a
PCM
64
4.1
G.711u
PCM
64
4.1
G.729
CS-ACELP
8
3.92
For
, quadruple the above mentioned rates (two fully duplex calls)
2N VoiceBlue MAX
®
and add the TCP and IP header transmission rate to the result to get the resultant
transmission rate.
It is important to keep both a stable appropriate transmission rate during connection
and a small and identical transmission time per data packet in order to maintain a high-
quality voice transmission.
G.711 – this codec is used in digital telephone networks. The PCM (Pulse Code
Modulation) is used for voice signal encoding. The sampled signal is encoded in
12 bits and then compressed using a non-linear scheme into the resultant 8 bits.
Europe uses the A-law compression system while North America and Japan
obey the µ-law. The resultant data flow is 64 kbps.
G.729 – this codec uses the CS-ACELP (Conjugate-Structure Algebraic-Code-
Excited Linear-Prediction) algorithm with the resultant transmission rate of 8
kbps. The speech signal is split into blocks of 10 ms each. The parameters of
these blocks are then inserted in frames of the size of 10 bytes. 2-byte frames
are generated for noise transmission.