6 Convenient Functions
6.4 Parallel Shift Job Conversion Function
6-28
155507-1CD
RE-CSO-A037
DX100
About 1 to 4 in the Table
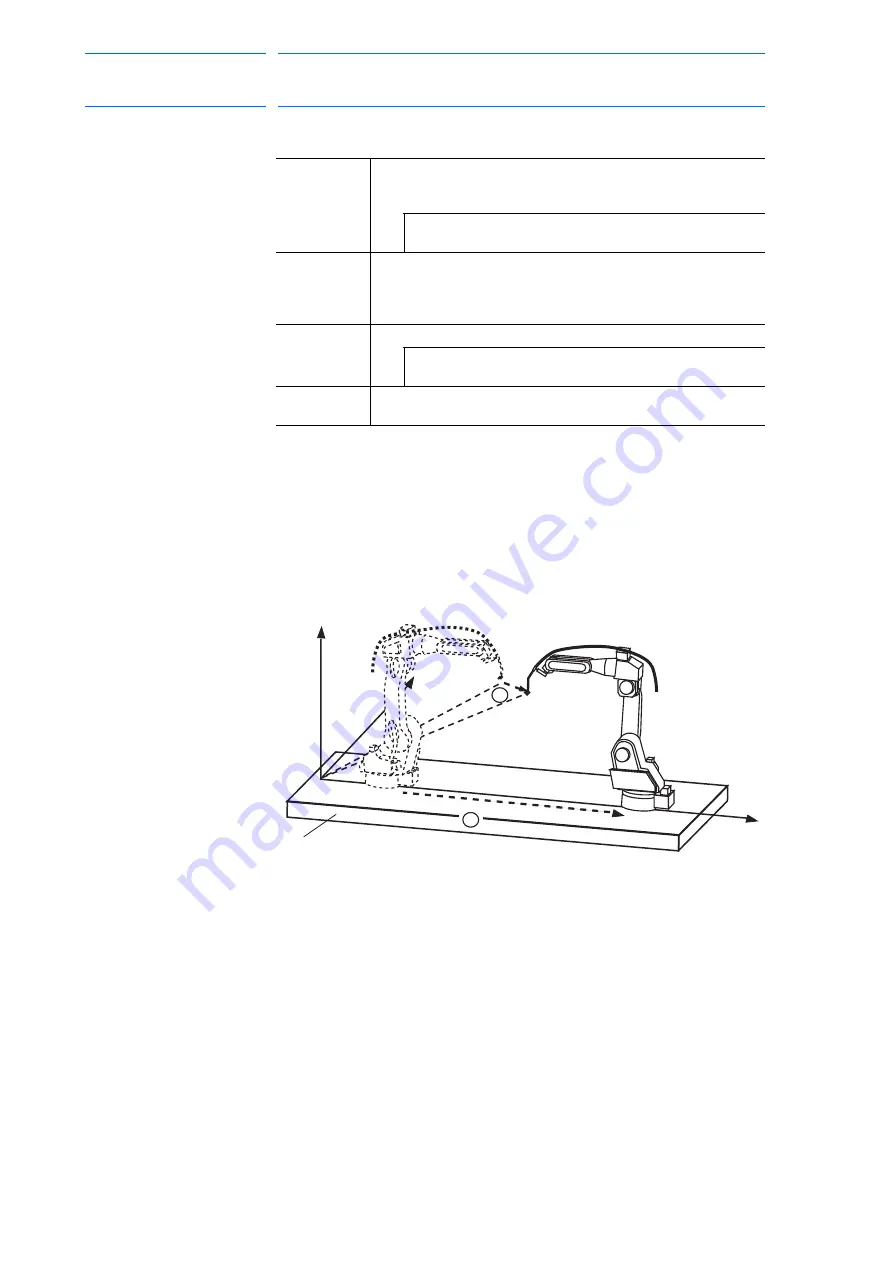
1. Base Coordinates
The base axis is shifted by B and the TCP of the manipulator is shifted
by A in the base coordinates.
R+S
The manipulator is shifted in the selected coordinates.
The station axis is shifted on the basis of pulse values regardless
of the coordinates.
Base coordinates, robot coordinates, tool coordinates, user
coordinates, pulse coordinates
R(B)+S
The manipulator is shifted in the selected coordinates, as in 1 to
5 above.
The station axis is shifted on the basis of pulse values regardless
of the coordinates.
R+R
Two manipulators are shifted in the selected coordinates.
Base coordinates, robot coordinates, tool coordinates, user
coordinates, master tool coordinates
1)
, pulse coordinates
R(B)+R(B)
Two manipulators are shifted in the selected coordinate system,
as in 1 to 5 above. Two base axes are also shifted.
1 In the master tool coordinates, conversion only occurs at the “slave” from the
standpoint of the SMOV instruction.
Table 6-2: Relationship Between Group Combinations and Coordinates at
Conversion
A
B
Base
Base coordinates
268 of 554






























