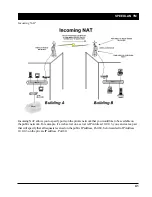
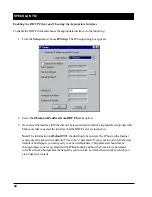
SPEEDLAN TM
29
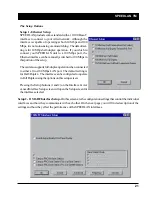
Storm Thresholds
- One of the unique and very useful features of the SPEEDLAN TM is its ability to keep
broadcast and multicast storms from spreading throughout a network. Network storms are common and can
cause bridges, routers, workstations, servers, and PCs to slow down or crash. Storms occur if network
equipment is configured incorrectly, if network software is not functioning properly, or poorly designed pro-
grams such as network games are used. These settings are disabled by default.
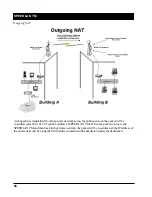
Enable Expanded IP ARP Support
- Enabling this feature will cause the Bridge to also watch the IP/ARP
packets that occur on the network. The SPEEDLAN TM takes no action in response to IP/ARP packets
(since that is the role of an IP router) except to add the IP address to its IP/ARP table. This feature is helpful on
an IP network because it will build a database of MAC-layer-address-to-IP address pairs. An SNMP moni-
toring program, such as the SPEEDLAN TM Configurator, can at any time extract this information. NOTE: 1)
The IP/ARP table is never timed out in this mode. 2) This feature is not available if the brouter is routing IP. The
default value for this setting is Disabled.
Permit Ethernet Broadcasts
- Standard Ethernet bridges will always forward broadcast packets. Many
protocols do not use broadcasts (e.g. AppleTalk Phase II, DECnet, and others). However, IP/ARP does use
broadcasts. If you do not use IP or any other protocol that requires broadcasts, you can deny them. Shutting
off broadcast packets will reduce the traffic being sent across your wireless network link. This will also greatly
reduce the number of interrupts that each computer connected to your network experiences. Networks with a
high number of broadcasts will slow down the processing of all attached computers, even those that aren’t
using the network.
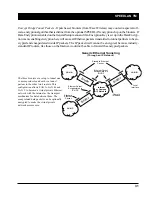
Enable Learned-Table Lockdown
- A standard bridge watches the source address of each packet it receives
on any of its interfaces. As new addresses are seen, entries are added to the
learned table
that contains each
source address and the interface number that address was received on. If a source address is later seen on a
different interface, the bridge will immediately change the interface number in the learned-table entry. This
condition could happen in a correctly functioning network if someone moved a computer to a different part of
the network. This could also happen if someone was trying to capture network packets by spoofing the bridge.
Enabling learned-table lockdown will prevent the interface number from being changed once the source ad-
dress has been seen. A standard bridge will also time-out the learned-table records every 10 minutes. If
learned-table lockdown is enabled, these records will not be timed out. Once a record is learned, it will not
change or be deleted until either the bridge reboots or the learned table become completely filled and needs to
be reset. (NOTE: A typical SPEEDLAN TM learned table can contain over 12,000 records.) The default
value for this setting is Disabled.
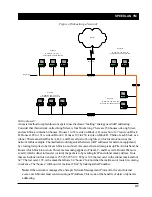
Pass Unseen Ethernet Source
- Standard Ethernet bridges will always forward packets with destination
addresses that have not been learned (i.e., have not previously been seen as a source address of a packet).
This characteristic is needed for the proper operation of an Ethernet bridge. The downside to this, as our
studies have shown, is that the failure mode of many Ethernet interface cards is to send out erroneous packets
with good CRCs but with random Ethernet destination and source addresses. Standard bridges will permit
these erroneous packets because they have not “learned” the random destination, and then add this packet’s
random source address to their finite learned table. This situation is not uncommon and can greatly hinder the
operation of standard bridges. If you choose to deny unlearned packets, the brouter will not forward unicast
packets to Ethernet addresses that have not already been seen as a source address. This scheme works for
most protocols because it relies on the characteristics of most upper-layer protocols to transmit ARP requests
or hello packets. It should be set to deny only by a qualified network engineer after careful testing and consid-
eration. The default value for this setting is checked.
Содержание SPEEDLAN TM 6000
Страница 2: ......
Страница 6: ......
Страница 7: ...SPEEDLAN TM INTRODUCTION...
Страница 8: ......
Страница 11: ...SPEEDLAN TM 11 USING CONFIGURATOR...
Страница 12: ......
Страница 15: ...SPEEDLAN TM 15 CONFIGURING SPEEDLAN TM...
Страница 16: ......
Страница 25: ...SPEEDLAN TM BRIDGING SETUP...
Страница 26: ......
Страница 32: ...SPEEDLAN TM 32...
Страница 33: ...SPEEDLAN TM 33 Setting Up the IP Addresses IP Host Setup...