LEXI-R422 - System integration manual
UBX-23007449 - R02
Design-in
Page 58 of 108
C1-Public
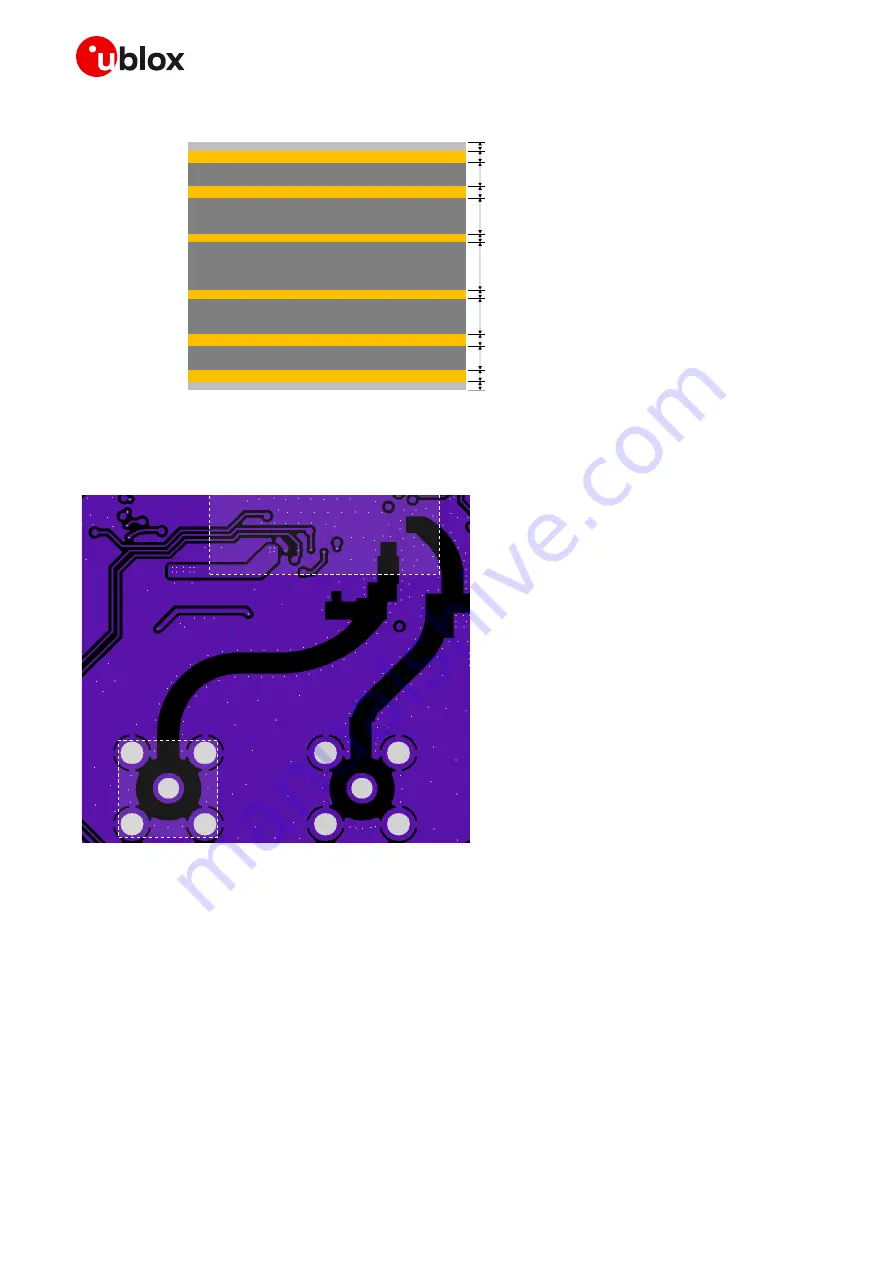
The PCB stack-up structure of the 6-layer u-blox host PCB is illustrated in
35 µm
35 µm
35 µm
35 µm
58 µm
58 µm
220 µm
Top layer (L1) copper
L5 copper
L2 copper
Bottom layer (L6) copper
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
Top layer (L1) solder
20 µm
20 µm
Bottom layer (L6) solder
18 µm
L3 copper
710 µm
FR-4 dielectric
18 µm
L4 copper
220 µm
FR-4 dielectric
Figure 36: Stack-up structure of the u-blox host PCB
Considering that the thickness of the dielectric material from the top layer to the buried layer is less
than 200 µm, GND keep-out is implemented on the buried metal layer area below the
ANT
pad and the
antenna RF trace as illustrated in
Figure 37: Buried metal layer (L2) layout of the u-blox host PCB, below the antenna RF trace design
Guidelines to design an equivalent proper connection for the
ANT
pad are available in section
Guidelines to design an equivalent proper 50
transmission line are available in section
Guidelines to design a proper equivalent 50
termination are available in section
, with further
guidelines for cellular antenna selection and design available in section
. Guidelines to design a
proper equivalent (optional) antenna detection circuit are available in section
The 50
characteristic impedance of the antenna trace design on a host PCB can be verified using a
Vector Network Analyzer, as done on the u-blox host PCB, with calibrated RF coaxial cable soldered at
the pad corresponding to RF input/output of the module and with the transmission line terminated to
a 50
load at the 50
SMA connector.
Compliance of the design with regulatory rules and specifications defined by the FCC, ISED, RED, etc.
can be verified using a radio communication tester (callbox) as the Rohde & Schwarz CMW500, or any
equivalent equipment for multi-technology signaling conformance tests.
















































