25
Sample Edit
Procedure
1 .
Press the [SAMPLE IMPORT] button.
The SAMPLE MENU screen appears.
2 .
Move the cursor to “SAMPLE EDIT” and press the [ENTER] button.
The SAMPLE EDIT screen appears.
3 .
Move the cursor to tab, and use the [
K
] [
J
] buttons to switch the pages.
4 .
Move the cursor to the parameter that you want to edit, and use the value
dial to change the value.
5 .
To save the edited settings, perform the operation “Saving Your Settings
(Write)” (refer to owner’s manual).
Sample Parameters
SAMPLE
NOTE
The following parameters cannot be edited for samples Sp:001–006 in the PRST
bank.
Parameter
Value/Explanation
Original Key
Specifies the note number that plays the sample at the pitch at which it
was imported.
C-1–G9
Loop Switch
Turns loop playback on/off.
OFF, ON
Start
Playback start point (Start Point) (*1)
This lets you skip an unwanted portion of the waveform at the beginning
of the sample so that the sample plays with the desired timing.
0–
Loop
Point at which the repeated portion starts on the second and subsequent
plays (Loop Point) (*1)
Specify this if you want to loop from a location other than Start After the
Sample played back from Start to End, it will then be repeatedly played
back in the forward direction, from the Loop to End.
0–
End
Playback end point (End Point) (*1)
This lets you omit an unwanted portion of the waveform at the end of the
sample.
0–
(*1)
The length of the imported sample is calculated, and the position of each point is shown as a
time (units: milliseconds).
The displayed value (time) is the value when the sample is played at the key specified by
Original Key. The playback time is shorter than displayed if you play a key that is higher than the
Original Key, and longer than displayed if you play a key that is lower.
TVF
Parameter
Value/Explanation
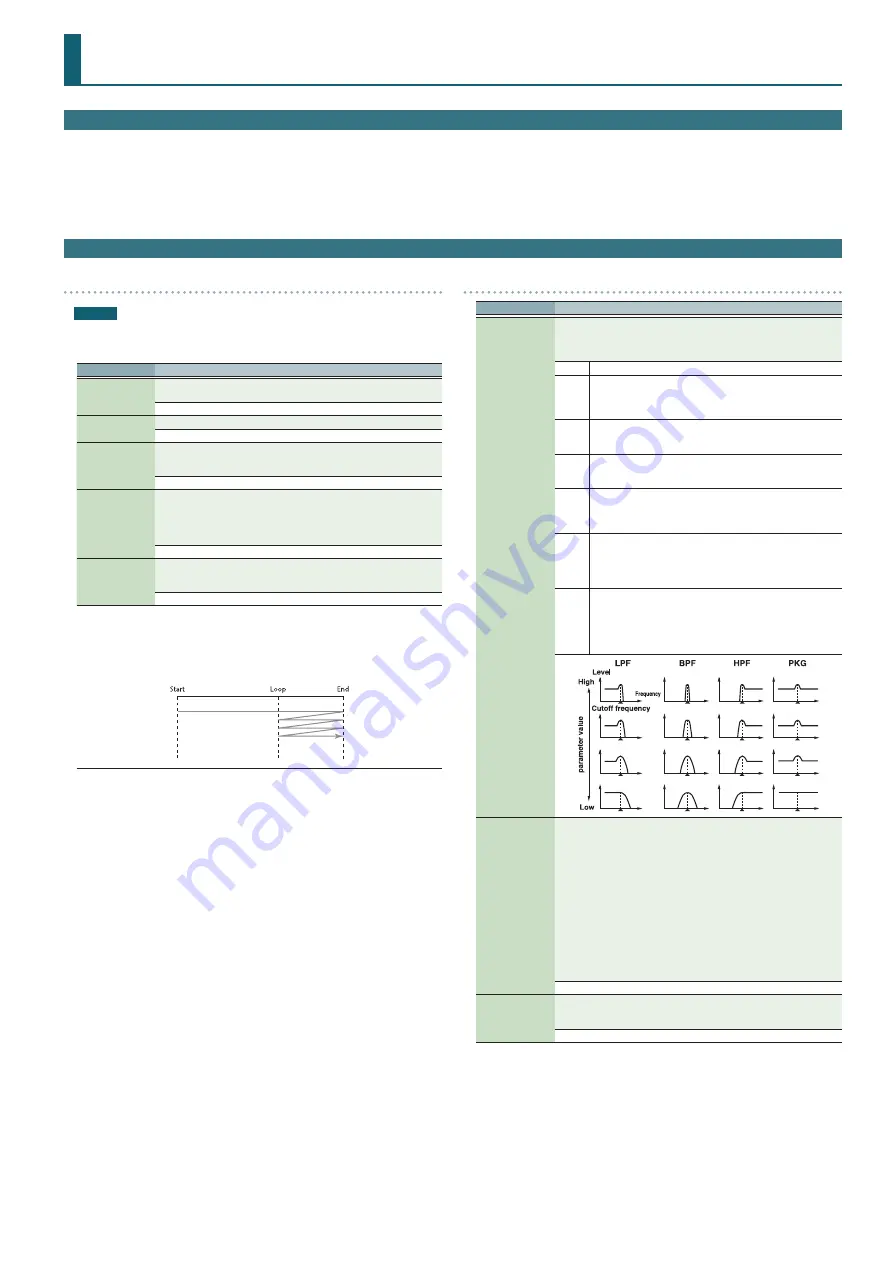
Filter Type
Selects the type of filter. A filter cuts or boosts a specific frequency region
to change a sound’s brightness, thickness, or other qualities.
*
If you set “LPF2” or “LPF3,” the setting for the Resonance will be ignored
OFF
No filter is used.
LPF
Low Pass Filter. This reduces the volume of all frequencies above
the cutoff frequency (Cutoff Freq) in order to round off, or un-
brighten the sound.
This is the most common filter used in synthesizers.
BPF
Band Pass Filter. This leaves only the frequencies in the region of
the cutoff frequency (Cutoff Freq), and cuts the rest. This can be
useful when creating distinctive sounds.
HPF
High Pass Filter. This cuts the frequencies in the region below
the cutoff frequency (Cutoff Freq). This is suitable for creating
percussive sounds emphasizing their higher tones.
PKG
Peaking Filter. This emphasizes the frequencies in the region of
the cutoff frequency (Cutoff Freq). You can use this to create wah-
wah effects by employing an LFO to change the cutoff frequency
cyclically.
LPF2
Low Pass Filter 2. Although frequency components above the
Cutoff frequency (Cutoff Freq) are cut, the sensitivity of this filter
is half that of the LPF. This makes it a comparatively warmer low
pass filter. This filter is good for use with simulated instrument
sounds such as the acoustic piano.
LPF3
Low Pass Filter 3. Although frequency components above the
Cutoff frequency (Cutoff Freq) are cut, the sensitivity of this filter
changes according to the Cutoff frequency. While this filter is
also good for use with simulated acoustic instrument sounds,
the nuance it exhibits differs from that of the LPF2, even with the
same TVF Envelope settings.
Cutoff Frequency
Selects the frequency at which the filter begins to have an effect on the
waveform’s frequency components.
“LPF/LPF2/LPF3” selected for the Filter Type
Lower cutoff frequency settings reduce a tone’s upper harmonics for a
more rounded, warmer sound. Higher settings make it sound brighter.
“BPF” selected for the Filter Type
Harmonic components will change depending on the TVF Cutoff
Frequency setting. This can be useful when creating distinctive sounds.
“HPF” selected for the Filter Type
Higher Cutoff Frequency settings will reduce lower harmonics to
emphasize just the brighter components of the sound.
“PKG” selected for the Filter Type
The harmonics to be emphasized will vary depending on Cutoff Frequency
setting.
0–127
Resonance
Emphasizes the portion of the sound in the region of the cutoff frequency,
adding character to the sound. Excessively high settings can produce
oscillation, causing the sound to distort.
0–127






























