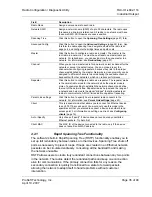
Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
RLX-IH
♦
802.11b
Industrial Hotspot
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Page 35 of 99
April 10, 2007
Field Description
Radio Name
Assign a unique name to each radio.
Network SSID
Assign a network name (SSID) of up to 32 characters. The radio uses
this name in all network references. All radios in a network must have
the same SSID. SSID names are case-sensitive.
Spanning Tree
Click this button to open the
Spanning Tree Settings
(page 37) form.
Advanced Config
Click this button to open the
Advanced Settings
(page 39) form. Use
this form to enable spanning tree, designate whether the radio is an
edge port, and configure the bridge times and path costs.
Master
Click this button to configure a radio as a master. The master is the
root radio in a network. You must have at least one master radio per
network. For redundancy, you can assign more than one master to a
network. For information, see
Redundancy
(page 37).
Channel
When you set up a master radio for a network, select a channel for the
network or accept the default value. You do not need to set the
channel when configuring repeaters, because they link to the proper
channel established by the master. Networks in close proximity can be
assigned to different channels to avoid sharing the available channel
bandwidth with other networks, which can reduce performance.
Repeater
Click this button to configure a radio as a repeater. The repeater mode
is the normal radio mode for the network, while the master mode is
more of a special setting to establish the network channel and define
the root of the network tree. Repeater radios help extend the range of
a network and help create the signal "bridges" that allow networked
radios to communicate. All RLX-IH radios are capable of repeating.
Parent Link settings
Click this button to specify how a repeater radio connects to the
network. For information, see
Parent Link settings
(page 40).
Client
This is a special mode that allows you to connect an Ethernet device
to any 802.11b access point. You would only use this mode in the
special event that you wanted to connect a device to another brand
access point. For information on setting up a client, see
Configuring
clients
(page 19).
Auto / Specify
Only choose "specify" if device does not send out any unsolicited
Ethernet packets. Try Auto first.
Client MAC
The MAC ID of the device connected to the radio, only if the device
does not advertise its MAC address.
4.2.1
Rapid Spanning Tree Functionality
The software's built-in Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) functionality enables you to
set up full redundancy between radios or other devices. Spanning Tree shuts off
ports as necessary to prevent loops. If loops are created in an Ethernet network,
packets can be circulated endlessly, consuming all the bandwidth and making
the network unusable.
RSTP allows users to create truly redundant connections between any two points
in the network. The radios detect the redundant paths and keep one connection
alive for communications. If the primary connection fails for any reason, the
secondary connection is quickly transitioned to a state to forward packets,
allowing the network to adapt itself to handle problems without customer
intervention.