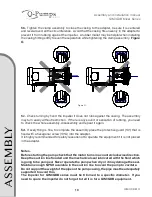
23
Assembly and installation manual
QIM/QDB Mixer Series
QIM/QDB-M01
QUICK GUIDE FOR SOLVING COMMON PROBLEMS
Q-Pumps products are relatively easy to maintain with the exception of the sanitary process.
Just as with any other element of machining, problems may arise. This section offers a
guide for identifying and correcting the majority of the pumping problems. For problems with you
motor, contact the manufacturer directly for best assistance.
The following table illustrates the problems and probable causes, assuming that the pump was
correctly selected for a specific application. If none of the listed solutions provided in the table resolves
the problem, the most likely cause is cavitation. Cavitation may be caused by an incorrect pump
selection and its symptoms include: excessive noise, insufficient pressure, fluid leak and vibration. If
these symptoms are bpresent, please re-evaluate your application.
1. NO FLOW
a) Motor speed too low.
b) Incorrect rotation direction.
c) Obstruction in discharge piping or closed valves.
2. INSUFICIENT FLOW
a) Motor speed too low.
b) Incorrect rotation direction.
c) Obstruction in discharge piping or closed valves.
d) Impeller damaged.
3. EXCESSIVE POWER CONSUMPTION
a) Motor speed too high.
b) Impeller damaged.
c) Motor shaft is bended or worn.
4. EXCESSIVE NOISE
a) Magnetic problem with motor.
b) Motor bearings damaged.
c) Foreign particles in impeller.
d) Impeller damaged.
e) Cavitation.
5. EXCESSIVE VIBRATION
a) Pump is not leveled.
b) Impeller damaged.
c) Piping lacks supports.
d) Cavitation.
6. FLUID LEAK
a) Disposable o-rings.
b) Disposable carbons.
c) Insufficient seal compression.
d) Damaged casing suction/discharge.
e) Disposable casing gasket.
f) Loose clamp assembly.
SOLUTIONS
a) Check electric connections and motor.
b) Reverse one of the motors three phases. If
direction does not change, contact manufacturer.
c) Remove obstruction and open valves.
a) Check electric connections and motor.
b) Reverse one of the motors three phases. If
direction does not change, contact manufacturer.
c) Remove obstruction and open valves.
d) Replace impeller.
a) Motor wires are bad, replace motor.
b) Remove casing and replace impeller.
c) Replace motor shaft.
a) Consult motor manufacturer.
b) Replace bearings.
c) Remove casing and extract particles.
d) Replace impeller.
e) Check system’s available NPSH.
d) Cavitation.
a) Level the pump.
b) Replace impeller.
c) Support suction and discharge piping.
d) Check system’s available NPSH.
a) Replace o-rings.
b) Replace carbons.
c) Replace spring.
d) Replace casing.
e) Replace casing gasket.
f) Tighten clamp assembly.
C
O
M
M
O
N
P
PR
O
B
LE
M
S