Point Grey Flea3 GigE Technical Reference
5 General Flea3 GigE Operation
5.2.1
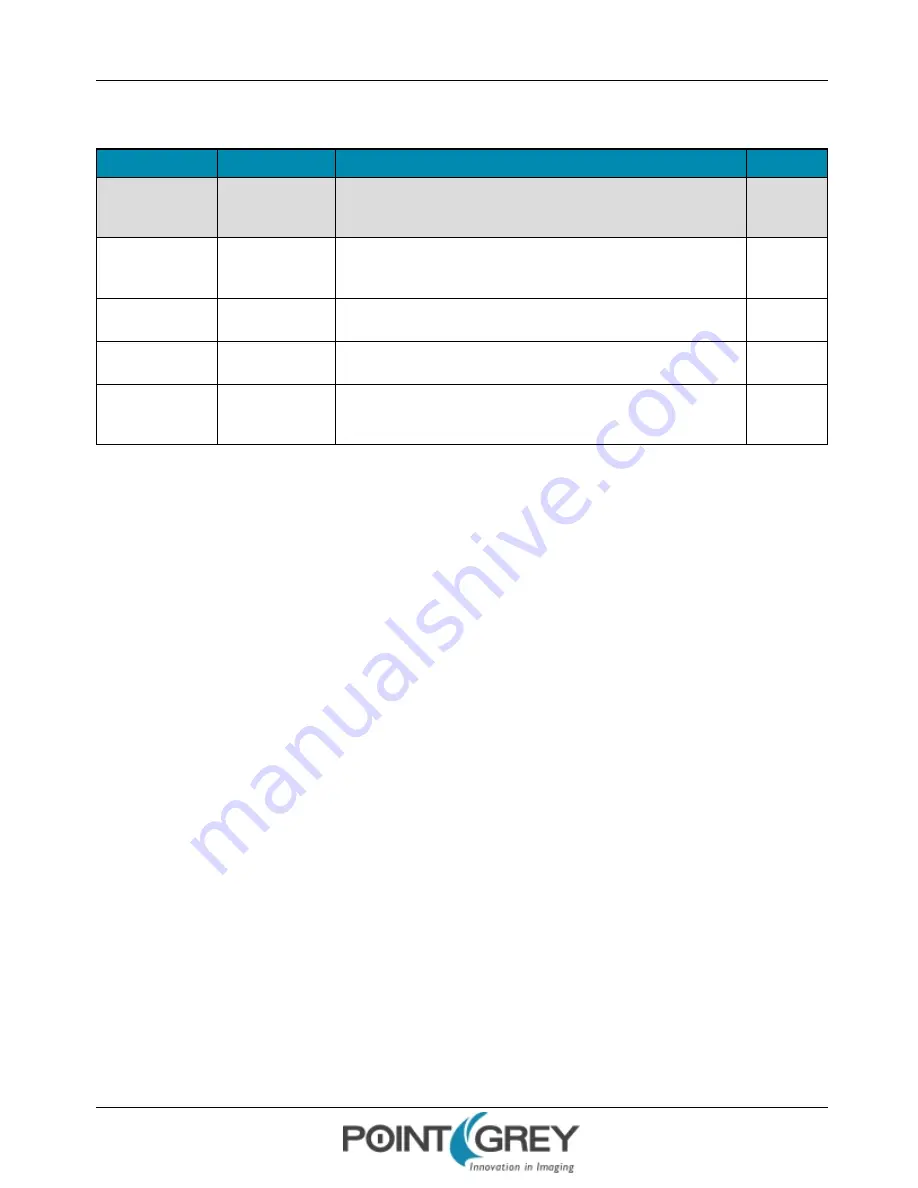
GenICam User Set Control
Name
Display Name
Description
Value
CurrentUserSet
Current User Set
Indicates the user set that is currently in use. At initialization time, the
camera loads the most recently saved user set
0 (default)
1
2
UserSetSelector
User Set Selector
Selects the user set to load or save
Default
User Set 1
User Set 2
UserSetLoad
User Set Load
Loads the user set specified by the User Set Selector to the device and
makes it active
Write Only
UserSetSave
User Set Save
Saves the user set specified by the User Set Selector to the non-volatile
memory of the device
Write Only
DefaultUserSet
Default User Set
Selects the default user set as the default start up set
Default
User Set 1
User Set 2
5.3
On-Camera Frame Buffer
The camera has a 32 MB that can be used for temporary image storage. This may be useful in cases such as:
n
Retransmission of an image is required due to data loss or corruption.
n
Multiple camera systems where there is insufficient bandwidth to capture images in the desired configuration.
All images pass through the frame buffer mechanism. This introduces relatively little delay in the system.
The user can cause images to accumulate by enabling the frame buffer. This effectively disables the transmission of
images in favor of accumulating them in the frame buffer. The user is then required to use the remaining elements of
the interface to cause the transmission of the images.
The buffer system is circular in nature, storing only the last 32 MB worth of image data. The number of images that this
accommodates depends on the currently configured image size.
The standard user interaction involves the following steps:
1.
Configure the imaging mode.
This first step involves configuring the format, mode and frame rate for acquiring images. This can be done by
either directly manipulating the registers or using the higher level functionality associated with the software
library being used. Depending on the software package, this may involve going so far as to configure the camera,
perform bandwidth negotiation and grab an image. In cases where bandwidth is restricted, the user will want to
disable transmission and free the bandwidth after the camera is configured.
2.
Enable frame buffer accumulation
The second step involves enabling the frame buffer. Enabling this results in images being accumulated in the
frame buffer rather than immediately being transmitted.
3.
Negotiate bandwidth with the camera
Having accumulated some number of images on the camera, bandwidth will have to be renegotiated if it has not
been done already. In most cases, this will involve effectively starting the camera in the imaging mode
configured in step (1).
4.
Disable isochronous transmission and enable buffered image transfer
To transfer buffered images, isochronous data transmission must be disabled, and transfer data enabled.
Revised 10/29/2013
Copyright ©2010-2013 Point Grey Research Inc.
28
















































