PCM-061/phyCORE-i.MX7 System on Module
L-821e_2
© PHYTEC America L.L.C. 2017
31
5
Real-Time Clock (RTC)
There are two options for an RTC on the phyCORE-i.MX7: the on-chip RTC or an external on-board RTC. If cost is the
primary concern, then the on-chip RTC should be considered to minimize external components. However, if power is the
primary concern, then consider using the external RTC to reduce power consumption. Typical VBAT power consumption
measurements for the RTC configuration options are provided in
Table 7
. The following sections detail these two RTC
options.
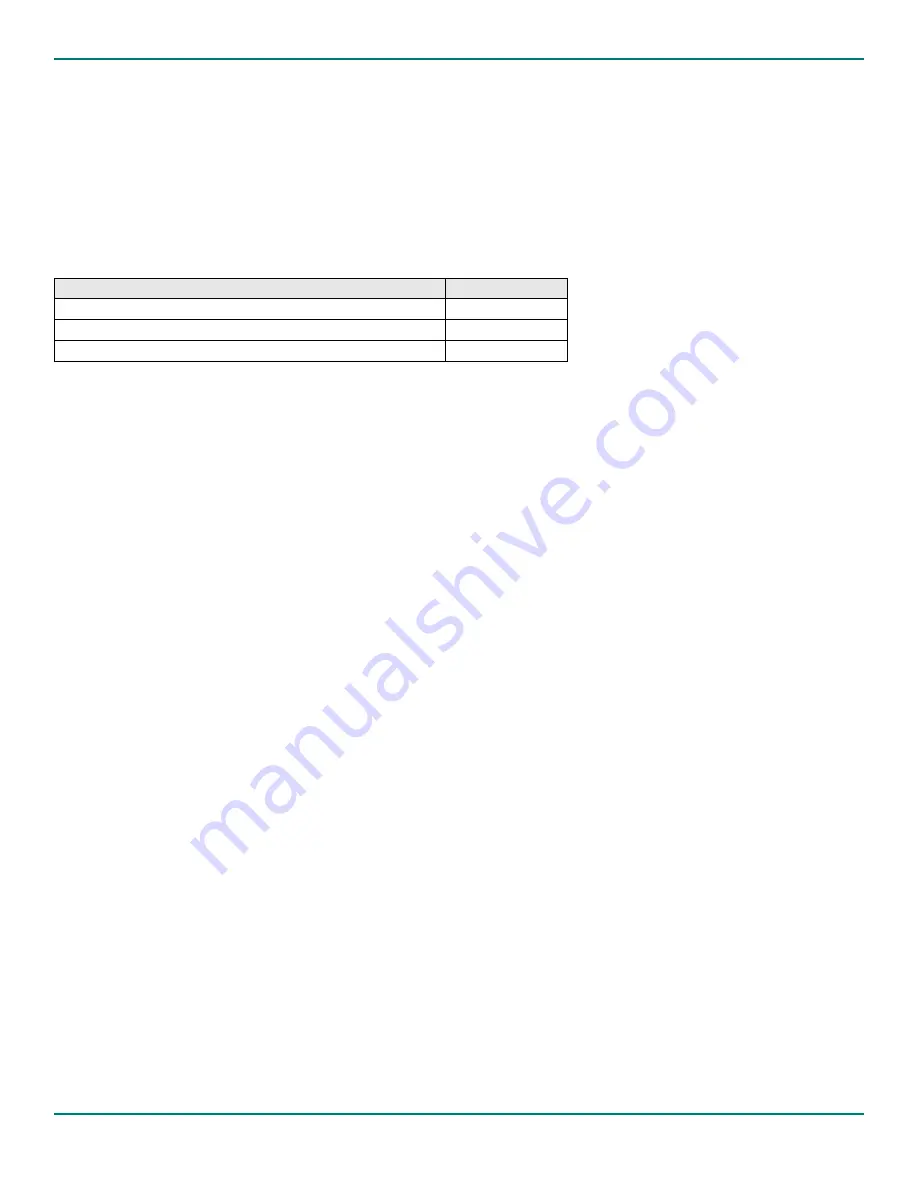
Table 7. Typical VBAT Power Consumption
RTC Configuration
I
VBAT
Typ. (uA)
Internal RTC Powered with External RTC Disconnected
34.99
External RTC Powered and Internal RTC Disconnected
1.32
Internal and External RTCs Powered
36.12
5.1
i.MX7 RTC
The i.MX7 processor includes an integrated RTC. However, the RTC integrated in the i.MX7 uses more power than the
external RTC on the SOM. Refer to the technical reference manual for further information.
5.2
External RTC
The SOM provides an ordering option to populate an external RTC at U10 which is connected to the I2C1 bus at address
0x68. The external RTC uses less power than the i.MX7 internal RTC, and can be used when very-low battery power is
critical. The external RTC typically uses 350nA at 3V. In order for the external RTC to maintain time when main system
power is removed, the VBAT input must be supplied with power. To achieve the lowest power consumption, resistor R172
must be removed to disconnect the PMIC VBAT backup supply. This can be accomplished via hand rework, or for series
production this component can be configured to be removed.
Jumper J24 is provided to configure the various interrupt options for the external RTC. By default, J24 is set to 1+2 so that
the interrupt is routed to a GPIO at the processor (pad EPDC1_DATA04).
Setting jumper J24 to 2+3 routes the interrupt to the X
_MX7_ONOFF signal to be used as a ‘wake’ signal.
Implement this
configuration for applications that use the RTC interrupt to transition the processor from a low power mode to RUN mode.
The jumper can also be set to 2+4 to route the interrupt to the PMIC PWRON pin to be used to trigger a PMIC power on
event. This configuration drives the PWRON input pin at the PMIC, allowing the RTC to bring the PMIC out of OFF and
Sleep modes. Use this configuration for applications that require the RTC interrupt to turn on the PMIC.













































