SERIE 5000
7
CONNECTIONS
3
CONNESSIONI
Calcolo del numero di diffusori (tramite le potenze)
Si supponga di avere definito sia l'amplificatore (cioè la sua potenza di
uscita) che il tipo di diffusore con relativa potenza assorbita.
In questo caso il massimo numero di diffusori collegabile sulla linea è
determinato dalla seguente formula:
numero diffusori
=
potenza amplificatore
potenza diffusore
Esempio
: si utilizzino un amplificatore
AW5240
con plafoniere modello
Paso C42
. L'amplificatore è in grado di erogare una potenza pari a
240 W, mentre un diffusore assorbe una potenza di 6 W.
Per sapere quanti diffusori sono collegabili alla linea di uscita si calcola:
240 W
6 W
numero diffusori
=
=
40
Determining the number of speakers (through power values)
If both the amplifier (i.e. its output power) and the type of speaker
with its power consumption have been established, the maximum number
of speakers which may be connected to the line may be determined as
follows:
number of speakers
=
amplifier power
speaker power
Example
: in a system including a
AW5240
amplifier with ceiling
speakers type
Paso C42
is used, the amplifier can supply 240 W power
whereas the speaker has a power consumption of 6 W.
The number of speakers which may be connected to the output line is
240 W
6 W
number of speakers
=
=
40
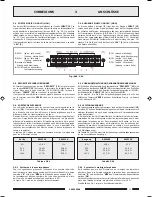
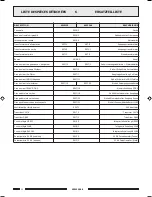
Calcolo dellimpedenza nei collegamenti in serie
Nel caso di diffusori collegati in serie tra loro, limpedenza totale è la
somma delle singole impedenze:
impedenza totale
=
Z1
+
Z2
+
Z3
+
....
Calcolo dellimpedenza nei collegamenti in parallelo
Nel caso di diffusori collegati in parallelo tra loro, limpedenza totale può
essere determinata mediante la seguente formula:
1
1
Z1
1
Z2
+
1
Z3
+
+ ......
impedenza totale
=
Calculating the impedance value in series connections
In the case of loudspeakers connected to one another in series, the total
impedance is the sum of the single impedance values:
Total impedance
=
Z1
+
Z2
+
Z3
+
....
Calculating the impedance value in parallel connection
In the event of loudspeakers connected in parallel to one another the
total impedance can be calculated by means of the following formula:
1
1
Z1
1
Z2
+
1
Z3
+
+ ......
Total impedance
=
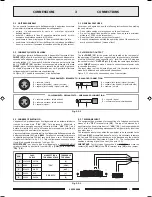
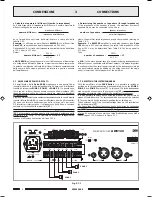
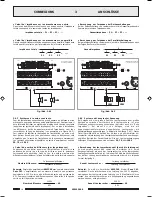
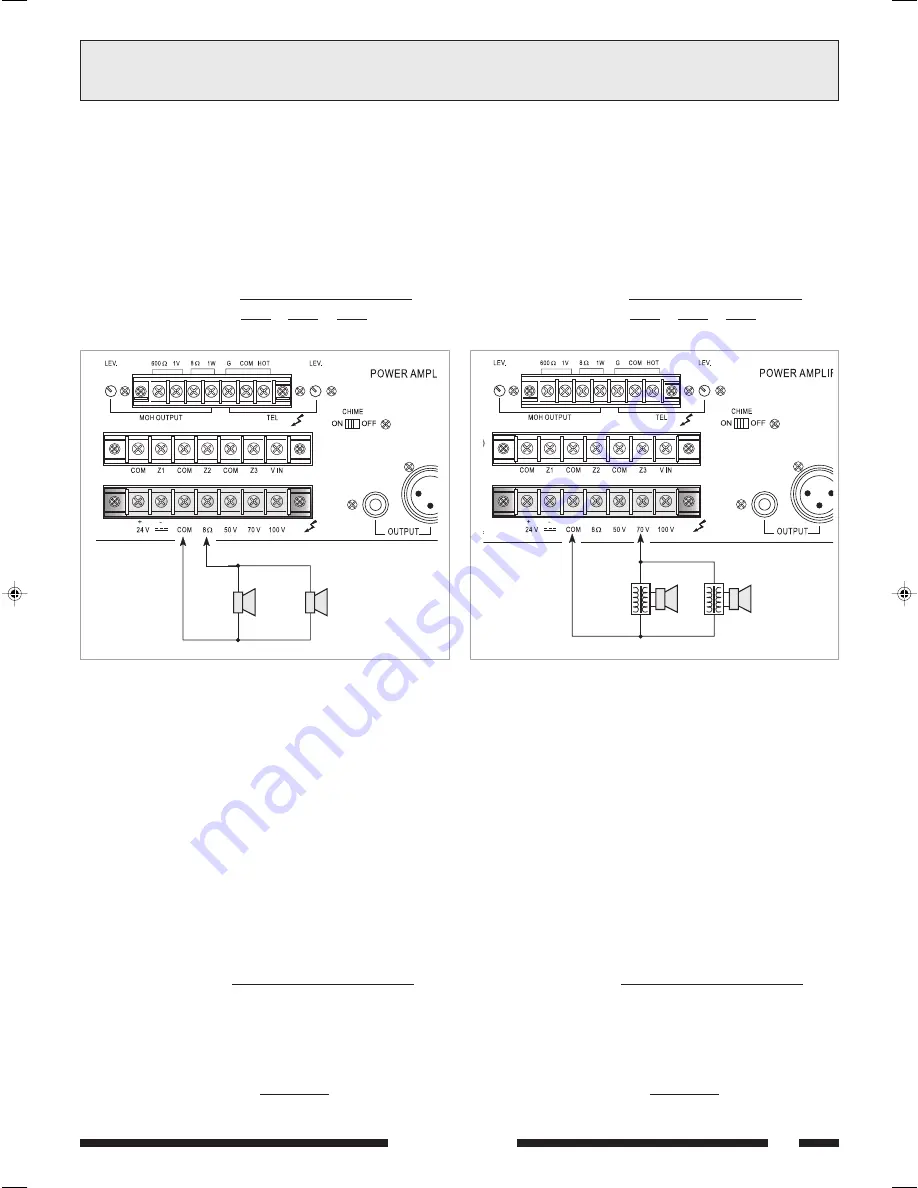
3.6.2 Sistemi a tensione costante
Nel caso di impianti con un gran numero di diffusori e/o con distanze tra
amplificatori ed altoparlanti molto elevate é preferibile utilizzare un sistema
di distribuzione a tensione costante (definito anche ad alta impedenza).
In questo tipo di impianto, i diffusori, provvisti di trasformatori di
adattamento di impedenza, sono tutti collegati in derivazione alla linea
(vedi es. di Fig. 3.6.2); questo particolare rende di facile realizzazione
limpianto e, nel caso in cui un altoparlante dovesse per qualche motivo
scollegarsi dalla linea, il resto dellimpianto proseguirebbe nel suo regolare
funzionamento. Le tensioni costanti disponibili in uscita dallamplificatore
sono
50
,
70
e
100 V
.
3.6.2 Constant voltage systems
When a large number of speakers is used and/or the speakers are
placed far from the amplifiers, constant voltage distribution system
should be used (also known as high-impedance systems).
In this type of system, the speakers are fitted with impedance
adaptation transformers and all of them have shunt line connections
(see example of Fig. 3.6.2). This simplifies the layout of the system and
if, for any reason, a loudspeaker is disconnected from the line, the rest
of the system will continue to work properly. The constant voltages
output from the amplifier are
50
,
70
and
100 V
.
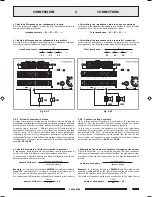
Fig. 3.6.1
Fig. 3.6.2
16
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
16
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
20W
20W
11-542.p65
26/10/01, 14.20
7