13 - EN
3.3 Mechanical Installation
3.3.1 General Requirements
Please familiarise yourself with the local regulations before considering any pipe-work installation as standards and specifications for pipe-work
systems can vary greatly from country to country. The information below is a guide based on installations performed within Europe.
Nitrogen, besides being inert, is also widely used because it is considered a clean dry gas.
Many of the processes that use nitrogen are of a critical nature and apart from contamination with oxygen, the removal of dirt particulate, oil and
water vapour from the gas stream is also essential. Therefore the pipe-work system and material that will transfer the nitrogen to it’s destination
should not add any unwanted contamination into the gas stream.
All components used within the system must be rated to at least the maximum operating pressure of the equipment. Buffer and nitrogen storage
vessels should be clean and free from oil and grease, and fitted with a suitable pressure gauge and pressure relief valve.
If there is any possibility of particulate contamination then this can be removed by installing a suitable Oil-X Evolution filter as near to the point of
use as possible. Ensure that each filter condensate drain is suitably piped away and any effluent is disposed of in accordance with local
regulations.
The compressed air feed pipe-work to the pre-treatment package should be suitable for compressed air duty and of a size and construction to
handle the maximum flow and pressures involved. Materials such as medium weight galvanized, Transair or similar are acceptable. As much
cutting fluid, oil and grease as possible should be removed from the pipe-work and fittings prior to connecting.
From the pre-treatment onwards and for the nitrogen gas, the pipe-work needs to be clean and oil-free.
If using a modular pipe-work system such as Transair, oil and grease should be removed using a suitable cleaner (if necessary) from the surfaces
that come into contact such as the pipe-work including fittings.
The most commonly used material for installing nitrogen pipe-work is table “X” de-greased copper. This should be silver soldered with a nitrogen
purge where ever possible and for threaded interfaces general heavy duty (GHD) fittings should be used. For small bore pipe-work, it is
sometimes acceptable to use compression type fittings or crimp type pipe-work systems. For food and pharmaceutical installations, welded or
threaded stainless steel is often specified, especially where it enters the production environment. For these market sectors the inclusion of sterile
filtration such as the “High Flow BIO-X” is advisable to ensure even the remote possibility of contamination from microorganisms is prevented.
In general flexible hoses should be avoided. They are almost certainly not suitable for high purity <100 ppm applications.
However, if they are to be used, ensure they are suitable for use with an inert gas. Certain materials such as nylon tubing can actually permeate
oxygen from outside to inside and affect the purity of the nitrogen gas. PTFE flexible tubing is preferred.
When routing the pipes ensure that they are adequately supported to prevent damage and leaks in the system.
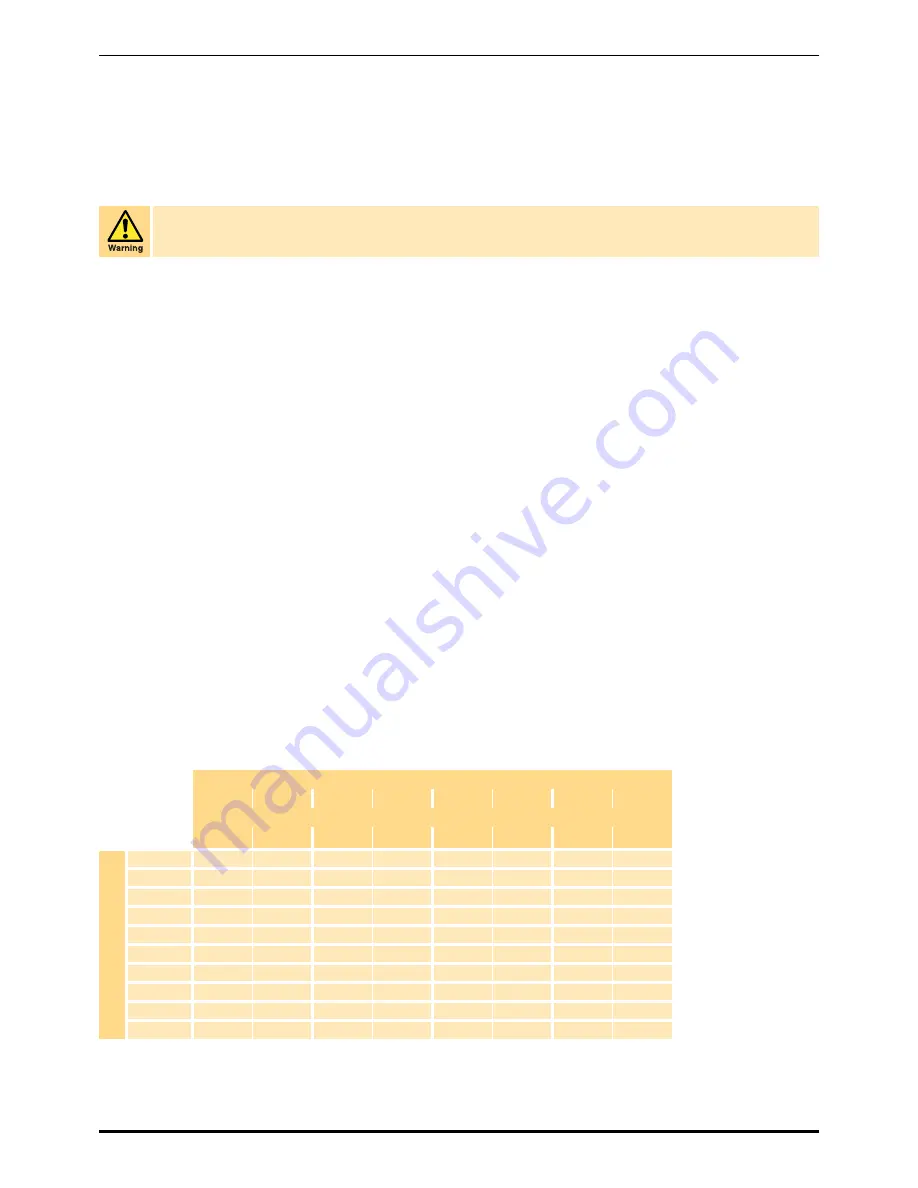
The diameter of the pipes must be sufficient to allow unrestricted inlet air supply to the equipment and outlet nitrogen supply to the application.
The following table gives guidance on the maximum recommended flow rates for smooth bore pipe-work.
The system must be protected with a suitably rated thermal pressure relief valve upstream of the generator.
Pressure
4 bar g
58 psi
6 bar g
87 psi
8 bar g
116 psi
10 bar g
145 psi
Recommended Flowrate
m
3
/hour
cfm
m
3
/hour
cfm
m
3
/hour
cfm
m
3
/hour
cfm
Pipe
s
ize I/
D (or
Equivalent)
16mm
28.8
17.0
43.2
25.4
64.8
38.1
75.6
44.5
20mm
36.6
21.5
57.6
33.9
82.8
48.7
101.0
59.4
25mm
68.4
40.3
111.0
65.3
155.0
91.2
194.0
114.2
32mm
152.0
89.5
227.0
133.6
295.0
173.6
385.0
226.6
40mm
306.0
180.1
432.0
254.3
576.0
339.0
702.0
413.2
50mm
440.0
259.0
698.0
410.8
940.0
553.3
1213.0
713.9
63mm
824.0
485.0
1318.0
775.7
1771.0
1042.4
2326.0
1369.0
75mm
1296.0
762.8
2034.0
1197.2
2847.0
1675.7
3510.0
2065.9
90mm
2052.0
1207.8
3186.0
1875.2
4576.0
2693.3
5490.0
3231.3
110mm
3600.0
2118.9
5652.0
3326.6
7956.0
4682.7
9756.0
5742.2
















































