www.netcommwireless.com
NetComm Wireless Light Industrial M2M Router Plus
25
Manually configuring a connection profile
To manually configure a connection profile:
1.
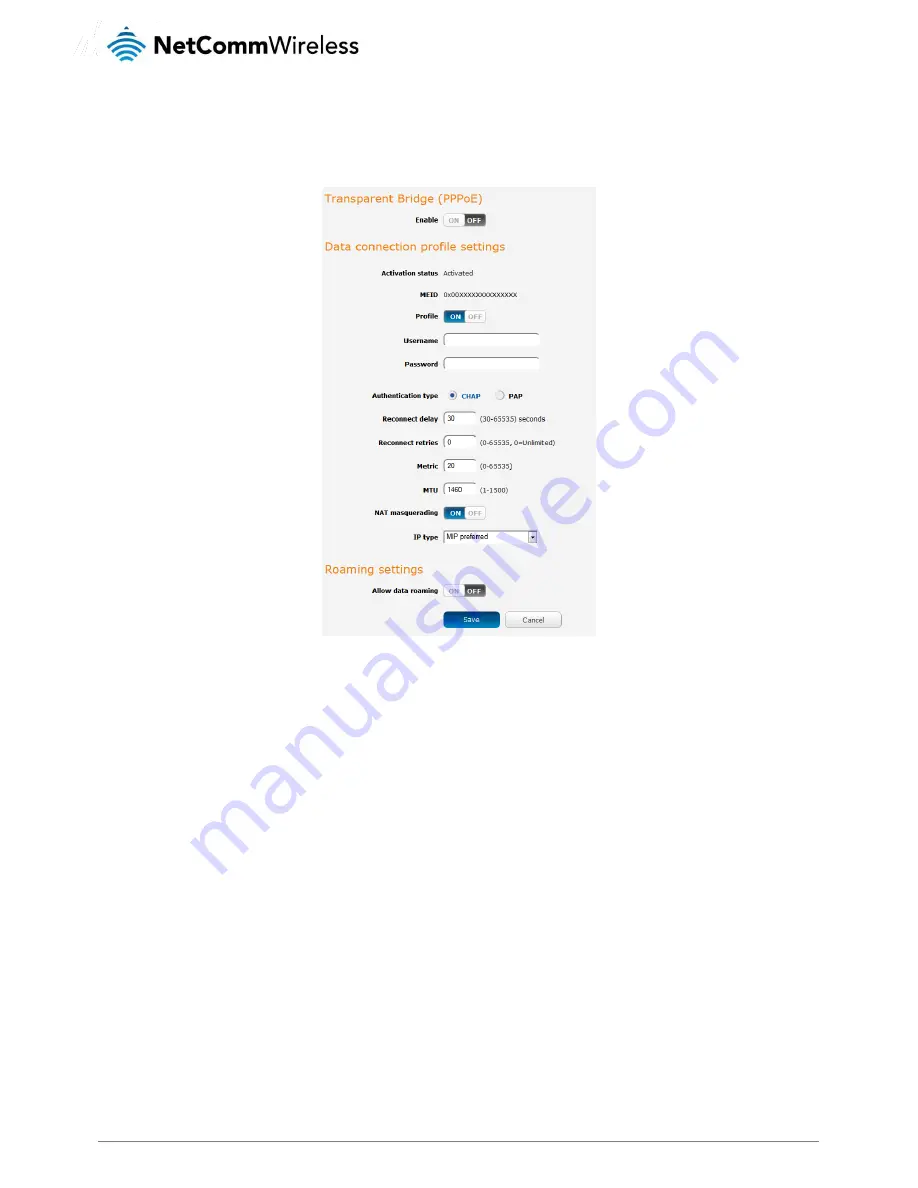
Click the Profile toggle key to turn the profile ON. Additional settings appear.
Figure 22 - Data connection settings - Profile turned on
2.
In the User and Password fields, enter the username and passwords assigned to your account by the carrier.
3.
Next to Authentication Type, select CHAP or PAP depending on the type of authentication used by your provider.
4.
The Reconnect Delay field specifies the number of seconds to wait between connection attempts. The default setting of
30 seconds is sufficient in most cases but you may modify it to wait up to 65535 seconds if you wish.
5.
The Reconnect Retries field specifies the number of times to attempt to connect to the network if the router fails to
establish a connection. It is set to 0 by default which causes the router to attempt to reconnect indefinitely.
6.
The Metric value is used by router to prioritise routes (if multiple are available) and is set to 20 by default. This value is
sufficient in most cases but you may modify it if you are aware of the effect your changes will have on the service.
7.
The MTU field specifies the maximum transmission unit which is the largest packet or frame that can be sent in a packet or
frame-based network such as the internet. The default value is 1460. This value should only be modified under instruction
from your carrier.
8.
Use the NAT Masquerading toggle key to turn NAT Masquerading on or off. NAT masquerading, also known simply as
NAT is a common routing feature which allows multiple LAN devices to appear as a single WAN IP via network address
translation. In this mode, the router modifies network traffic sent and received to inform remote computers on the internet
that packets originating from a machine behind the router actually originated from the WAN IP address of the router’s
internal NAT IP address. This may be disabled if a framed route configuration is required and local devices require WAN IP
addresses.
9.
Use the IP Type drop down list to select the type of IP that you want the router to create. SIP Only creates a Simple IP via
Point-to-Point Protocol and if the router moves between cell sectors, the packet data link is lost. MIP Only establishes a
Mobile IP connection using an address which is persistent across cell sectors, allowing the router to move between
sectors without losing the packet data link. MIP Preferred sets the router to use a Mobile IP where possible, but allowing a
Simple IP connection if MIP is not available.
10.
Click the Save button when you have finished entering the profile details.






























