1-22 Technical Information
PCI devices are categorized as follows to specify their interrupt grouping:
INTA
By default, all add-in cards that require only one interrupt are in this category.
For almost all cards that require more than one interrupt, the first interrupt on the
card is also classified as INTA.
INTB
Generally, the second interrupt on add-in cards that require two or more
interrupts is classified as INTB. (This is not an absolute requirement.)
INTC and INTD
Generally, a third interrupt on add-in cards is classified as INTC and a fourth
interrupt is classified as INTD.
The PIIX4 PCI-to-ISA bridge has four programmable interrupt request (PIRQ) input
signals. Any PCI interrupt source (either onboard or from a PCI add-in card) connects to
one of these PIRQ signals. Because there are only four signals, some PCI interrupt sources
are mechanically tied together on the system board and, therefore, share the same interrupt.
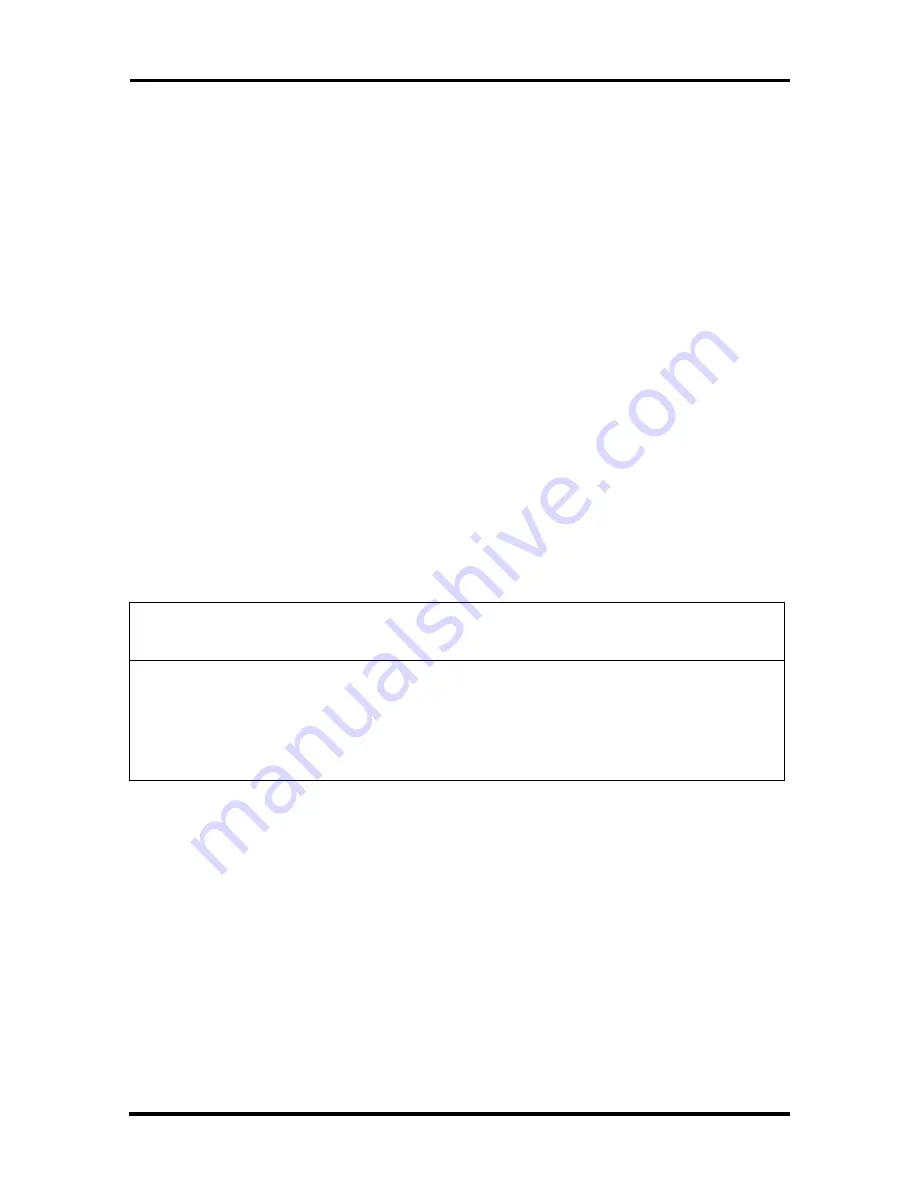
Table 1-9 lists the PIRQ signals and shows how the signals are connected to the PCI
expansion slots and to onboard PCI interrupt sources.
Table 1-9 PCI Interrupt Routing Map
PIIX4
PIRQ
Signal
First PCI
Expansion
Slot: J1D2
Second PCI
Expansion
Slot: J1D1
Third PCI
Expansion
Slot: J1C1
Fourth PCI
Expansion
Slot: J1B1
AGP
USB
LAN
SCSI
Power
Mgmt
PIRQA INTD
INTC
INTB
INTA
INTA
X
PIRQB INTA
INTD
INTC
INTB
INTB
X
PIRQC INTB
INTA
INTD
INTC
PIRQD INTC
INTB
INTA
INTD
X
X
For example, assume an add-in card has one interrupt (group INTA) into the second PCI
slot (J1D1). In this slot, an interrupt source from group INTA connects to the PIRQC
signal, which is not connected to any onboard interrupt sources. If there are no other add-in
cards, this card does not share its interrupt with any other devices.
Now, however, plug a second add-in card that has two interrupts (group INTA and INTB)
into the first PCI slot (J1D2). INTA in the first slot is connected to signal PIRQB and INTB
is connected to signal PIRQC. Therefore, the second device on the two-function add-in
card in the first slot will share its interrupt with the single-function card in the second slot.
In addition, the first device on the two-function add-in card in the first slot will share its
interrupt with the on-board SCSI controller and second device on a multi-function AGP
add-in card.
















































