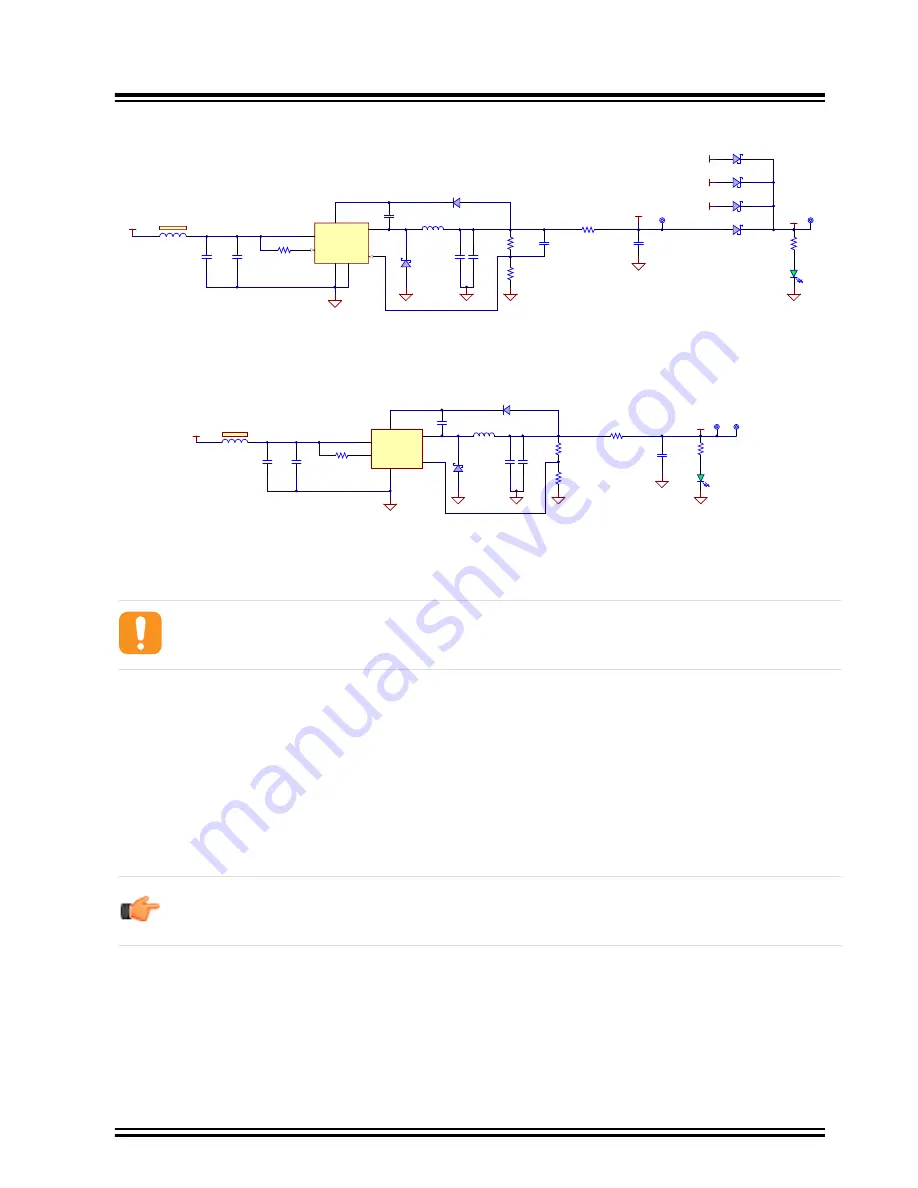
Figure 3-12. 5V Voltage Design
5V
GREEN
D9
GND
500mA max
5 Volts
VDC
GND
GND
GND
TP6
TP5
GND
0.1uF
C53
B140-13-F
D8
10uF
C56
10uF
C57
5V Buck Conver ter
470R
FB3
VBUS_JLINK
VUSB
22uH
L4
1N4448
D6
560R
0402
5%
R12
1M
R14
10k
0402
1%
R15
20pF
50V
0402
C54
6V to 48V
MBR0520
D7
MBR0520
D3
MBR0520
D4
5V_REG
5V_XPLAIN
MBR0520
D5
BOOST
7
GND
5
VFB
6
EN
2
SW
1
VIN
8
E
P
9
MCP16331
U2
1uF
C55
GND
0R
R11
10uF
75V
1210
C58
10uF
75V
1210
C59
56k
0402
1%
R13
Another buck converter, MC16301, is used to generate a regulated 3.3V voltage rail required by the PL485. For a
further description about the buck converter see the
.
Figure 3-13. 3.3V Buck Converter Design
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
D
D
C
C
B
B
A
A
3 of 6
PL485 - Evaluation Kit
05/12/2019 15:01:59
Power Supply.SchDoc
Project Title
Sch #:
Date:
File:
Revision:
Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
JLCF
Sheet Title
Power Supply
Engineer:
JLCF
03-PL485
B
Size
A3
PL485-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
CEN-B
Altium.com
5V
GREEN
D9
GND
GND
500mA max
5 Volts
VDC
GND
GND
TP6
TP5
TP4
TP7
GND
0.1uF
C53
B140-13-F
D8
10uF
C56
10uF
C57
5V Buck Conver ter
TP8
470R
FB3
3V3
GREEN
D12
GND
600mA max
3.3 Volts
5V
GND
GND
GND
TP10 TP11
GND
0.1uF
C60
B140-13-F
D11
10uF
C61
10uF
C62
15uH
L5
3V3 Buck Conver ter
TP9
470R
FB4
VBUS_JLINK
2
3
1
POWER 2.0mm
J3
VUSB
22uH
L4
1N4448
D6
1N4448
D10
560R
0402
5%
R12
52.3k
0402
1%
R13
1M
R14
1M
R19
300R
R18
10k
0402
1%
R15
10k
0402
1%
R20
31.6k
0402
1%
R17
20pF
50V
0402
C54
6V to 48V
MBR0520
D7
MBR0520
D3
MBR0520
D4
5V_REG
GND
VDC
TP3
0.1uF
100V
1206
C50
4.7uF
100V
1210
C49
SMBJ51A
D2
BOOST
1
GND
2
VFB
3
EN
4
SW
6
VIN
5
MCP16301T-I/CHY
U3
4.7uF
50V
1210
C64
4.7uF
50V
1210
C65
PMEG6010ER
D1
4A
F1
1
2
J2
PLC Connector
GND_IN
5V_XPLAIN
MBR0520
D5
Power Supply
560uH
L2
560uH
L3
0.1uF
100V
1206
C52
GND
GND_IN
BOOST
7
GND
5
VFB
6
EN
2
SW
1
VIN
8
E
P
9
MCP16331
U2
PLC+
PLC-
6V to 48V
1uF
C63
1uF
C55
GND
GND
0R
R16
0R
R11
0R
R9
0R
R10
50V
MOV1
10uF
75V
1210
C51
10uF
75V
1210
C58
10uF
75V
1210
C59
DC IN
DC Input
There is one LED and two test points on each voltage rail to check whether all power supplies are operating properly.
To avoid on board self-generated disturbances within the PLC signal band, both converters are switching at 500 kHz
fixed frequency, out of the PLC band (95 to 125 kHz).
Attention:
To avoid noise interferences, the switching frequency of the external SMPS must be out of the
PLC band and preferably in frequencies above it to avoid harmonics influence. This is essential to obtain a
good reception performance.
3.6 Hardware Description - JLINK Debugger
for information about +3.3V LDO to supply J-
Link.
3.3.5.1
PLC Rejection Filter
As the PLC coupling circuit is in parallel with the power supply circuit, the input impedance of the final equipment
could be affected. If the requirements about total input impedance are not satisfied, an appropriate input filter is
needed at the power supply input to increase the input impedance.
Besides the input filter, it is also recommended to add a PLC rejection filter to avoid the absorption of the PLC signals
by the power supply circuit. This filter also increases the input impedance, so it helps to achieve the requisites about
input impedance.
Notice:
The PL485-EK board has PLC coupling and power supply circuits in parallel, so the PLC
rejection filter is included. A PLC rejection filter is needed in case of low input impedance after connecting
in the same point the PLC Coupling connector J2 and the power source of the board.
The PLC rejection filter of the PL485-EK is composed of two inductors in-series (L = 560 μH) and a capacitor in-
parallel (C = 0.1 μF) at the power supply input as shown in the following picture.
PL485-EK
PL485-EK Board
©
2020 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002954B-page 19















































