Installation and Operational Instructions for
ROBA-stop
®
-S brake Type 856. _ _ _ . _
Size 11
(B.8.3.1.GB)
19/11/2010 TK/KE/GC/SU
Chr. Mayr GmbH + Co. KG
Tel.: 08341 / 804-0
Eichenstraße 1
Fax: 08341 / 804-421
D-87665 Mauerstetten
http://www.mayr.de
Page 12 of 13
Germany
E-Mail:
Braking Torque Adjustment (Figs. 1 to 3)
The ROBA-stop-S brake Size 11 is set manufacturer-side to the
nominal torque or to the braking torque stipulated on order.
Braking torque adjustment is carried out by evenly removing or
adding thrust springs (6 and 29) to the internal or external pole of
the coil carrier (2) acc. Table 1.
DANGER
By removing the brake plate (16), the braking
torque is nullified. Load movement must be
prevented.
Procedural Method:
1. Remove the brake plate (16) by loosening the hexagon
head screws (17). Please observe the adjusting plates (28).
If necessary, use the emergency release screws (9) as a
removal aid. In this case, the screw plugs (10) with the
copper sealing rings (11) must be unscrewed and screwed
in again after brake plate (16) removal.
2. Remove the rotor (4).
3. Evenly loosen the 3 cap screws (7), which together with the
collar bushings (8) hold (guide) the armature disk (5) axially,
until the armature disk (5) can be removed.
Danger! The armature disk is subject to spring pre-
tension!
4. Remove abraded particles from the rotor and clean the
brake.
Do not use grease or oil!
5. Adjust the required braking torque by evenly removing or
adding thrust springs (6 and 29) to/from the coil carrier (2)
(see Table 1).
One spring (6) at the internal pole equals
102 Nm.
One spring (29) at the external pole equals
61 Nm.
The thrust springs (6) at the internal pole of the
coil carrier and the thrust springs (29) at the
external pole of the coil carrier must not be
interchanged (see Table 1).
6. Insert the armature disk (5).
Please make sure that the two pins for actuating the
microswitch situated next to each other protrude into
the terminal box.
7. Screw the armature disk (5) back on using cap screws (7)
and added collar bushings (8).
Observe the tightening torque of 85 Nm!
8. Push the rotor (4) back on. Check that the toothing moves
easily.
The rotor (4) must be placed onto the hub (1)
so that the toothing remains engaged even after
wear on the friction linings.
9. Mount the brake plate (16) again using hexagon head
screws (17). Please make sure that the emergency release
has the correct angular position (see Fig. 2).
Do not damage the O-rings (18 and 19)!
Observe the tightening torque of 46 Nm!
Table 2: Spring Configuration
Number of springs Ø 22 / 4,5 x 50
at internal pole (Item 6)
Torque on
brakes
[Nm]
2
3
4
5
2
326
428
530
632
3
387
489
591
693
4
448
550
652
754
N
u
m
b
e
r
o
f
s
p
ri
n
g
s
Ø
1
9
/
3
,6
x
3
8
a
t
e
x
te
rn
a
l
p
o
le
(
It
e
m
2
9
)
5
509
611
713
815
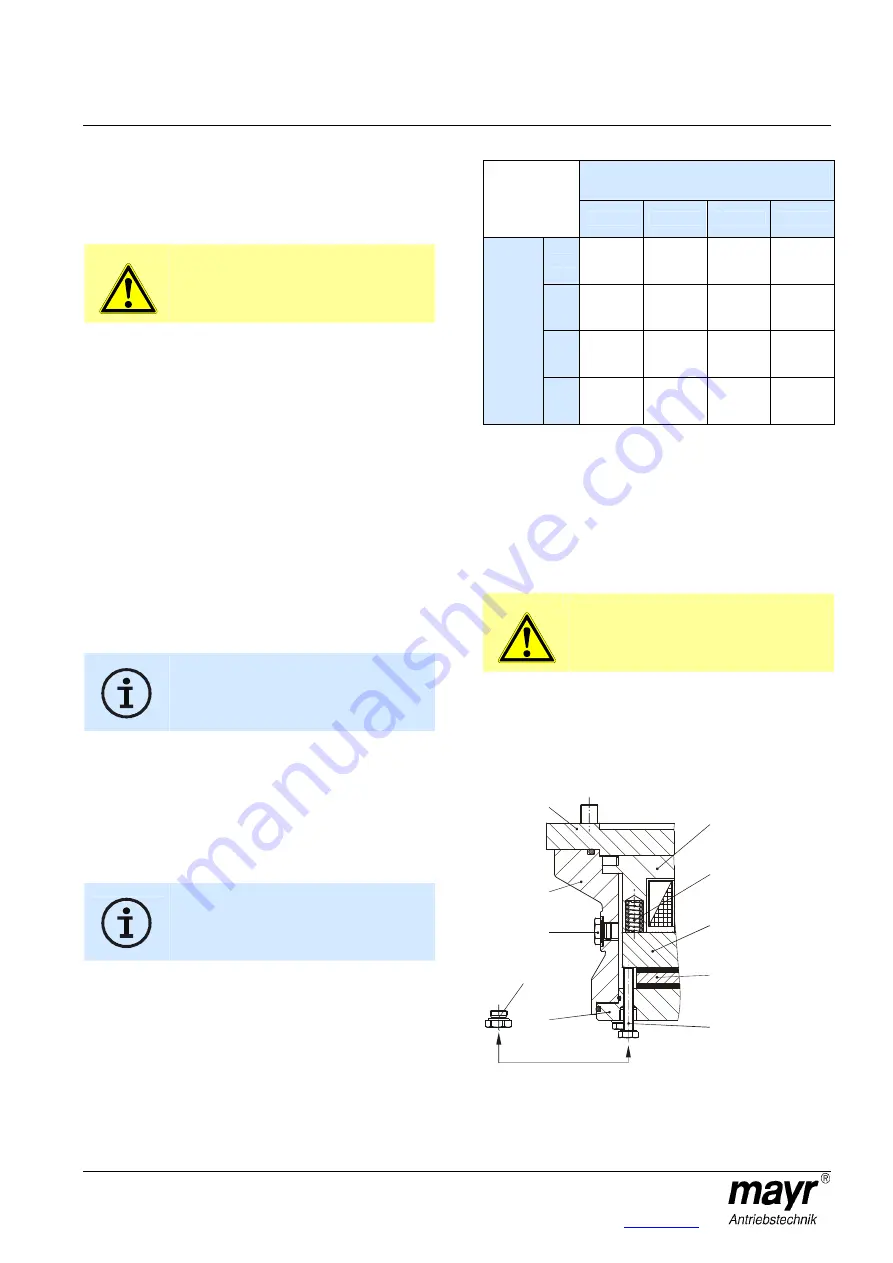
Emergency Release (Fig. 13)
In case of malfunction or power failure, the brake remains
closed; it cannot be released electrically. Emergency release can
be carried out manually.
1. Unscrew the screw plugs (10) inc. the copper sealing rings
(11).
2. Screw in both emergency release screws (9) evenly until the
load on the motor starts moving.
DANGER
Caution with hoist drives!
Actuating the emergency release nullifies the
braking torque.
Load crashes must be prevented.
Interrupt the release procedure with individual stops (turning
back the emergency release screws), so that there is no
high load acceleration and brake heating occurrence.
3. After completing the emergency release procedure, unscrew
both emergency release screws (9) again.
4. Screw the screw plugs (10) inc. the copper sealing rings
(11) back in.
Fig. 13
29
4
9
5
2
3
16
31
12/13
10/11













