©
2010 Magnum Energy, Inc
Page 15
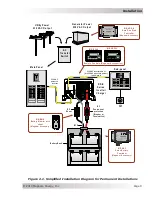
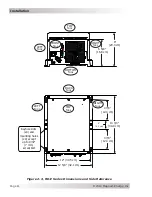
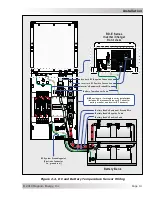
Installation
2.4.1
DC Wire Sizing
It is important to use the correct DC wire to achieve maximum ef
fi
ciency from the system and
reduce
fi
re hazards associated with overheating. Always keep your wire runs as short as practical
to help prevent low voltage shutdowns and keep the DC breaker from nuisance tripping (or open
fuses) because of increased current draw. See Table 2-1 to select the required minimum DC wire
size (and corresponding overcurrent device) based on your inverter model. The cable sizes listed
in Table 2-1 for your inverter model are required to reduce stress on the inverter, minimize voltage
drops, increase system ef
fi
ciency, and ensure the inverter’s ability to surge heavy loads.
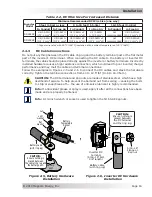
If the distance from the inverter to the battery bank is greater than 5 feet (1.5 m), the DC wire
size will need to be increased. Longer distances cause an increase in resistance, which affects the
performance of the inverter. Continue to use the overcurrent device previously determined from
Table 2-1, and then refer to Table 2-2 to determine the minimum DC wire size needed for various
distances based on your inverter model.
2.4.2
DC Overcurrent Protection
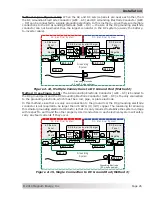
DC overcurrent protection is not included in the inverter, it
must
be provided as part of the
installation. This requirement is needed in order to comply with electrical code regulations and
for safety reasons. The DC overcurrent protection device must be installed in the positive DC
cable line, it can be a fuse or a circuit breaker, and it must be DC rated. It must be correctly sized
according to the size of DC cables being used, which means it is required to open before the cable
reaches its maximum current carrying capability, thereby preventing a
fi
re. The NEC requires both
overcurrent protection and a disconnect switch. If a circuit breaker is used as the overcurrent
protection device, it can also be used as the required DC disconnect.
If a fuse is used as an overcurrent device, a Class-T type or equivalent is recommended. This fuse
type is rated for DC operation, can handle the high short-circuit currents, and has a time delay
that allows for momentary current surges from the inverter without opening the fuse. However,
because the fuse can be energized from both directions, if it is accessible to unquali
fi
ed persons
the NEC requires that it be installed in such a manner that the power must be disconnected on
both ends of the fuse before servicing.
The recommendations in Table 2-1 may not meet all local code requirements.
Note 1 - Maximum Continuous Current is based on the inverter’s continuous power rating at the lowest input
voltage with an inef
fi
ciency factor.
Note 2 - Wire size is based on the requirements needed to increase ef
fi
ciency and reduce stress to the inverter.
Note 3 - The next larger standard size overcurrent device may be used if the de-rated cable ampacity falls between
the standard recommended overcurrent devices.
Note 4 - As recommended, the DC grounding electrode conductor can be a #6 AWG (33.6 mm2) conductor if that is the
only connection to the grounding electrode and that grounding electrode is a rod, pipe, or plate electrode.
Note 5 - May not allow continuous operation at full rated power.
Table 2-1, Recommended DC Wire/Overcurrent Device for Rated Use
Inverter
Model
Maximum
Continuous
Current
1
Using Conduit
DC Grounding
Electrode
Wire Size
4
Minimum DC Wire
Size (90°C
rating)
2
Maximum DC
Breaker Size
3
RD2624E
173 amps
#4/0 AWG
[107.2 mm
2
]
(260 amps)
250 amps
#6 AWG
(13.3 mm
2
)
RD4024E
267 amps
#4/0 AWG
[107.2 mm
2
]
(260 amps)
250 amps
#6 AWG
(13.3 mm
2
)