Input Synchronization
2-15
•
S5 again test the detection of S after period P. If S is detected,
transition “a” leads back to synchronized state S3. If not, transition
“b” leads back to S0 to look for another sync location.
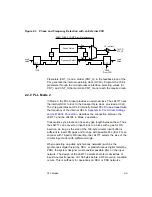
To review the transitions in the sync acquisition and sync tracking
phases:
•
Transition a0 occurs when word S is detected.
•
Transition b0 occurs when word S is not detected.
•
Transition “a” occurs when word S is detected exactly P bytes after
the last detection test.
•
Transition “b” occurs when word S has not been detected P bytes
after the last detection test. This transition activates a declaration of
loss-of-sync.
The L64777 activates output SYNCOK in state S3, S4, or S5. This allows
easy measurement of synchronization conditions from outside and
monitoring during normal operation. The microprocessor interface also
provides SYNCOK information. At this interface, the L64777 can read the
actual status and a glitch trap (which detects any sync losses between
two sync status reads). SYNCOK can also generate interrupts, if the
SYNCOK interrupt is not masked (see Section 4.2.1, “Register 12,”
page 4-10).
In order to use a subset of the device with random data (without frame
structure), bypass the synchronization mechanism by setting the
unconstrained bit in the register map (see Section 4.1.10, “Register 11,”
page 4-9).
Содержание L64777
Страница 1: ...L64777 DVB QAM Modulator Order Number I14031 A Technical Manual June 2000...
Страница 10: ...x Contents...
Страница 14: ...1 4 Introduction...
Страница 90: ...5 10 Signals...
Страница 110: ...A 8 Programming the L64777 in Serial Host Interface Mode...
Страница 116: ...C 2 Monitoring Device Internal Signals...
Страница 124: ......