Page 22
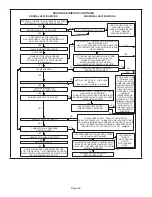
H- Proper Ground and Voltage
A poorly grounded furnace can contribute to poor flame
sense signal. Use the following procedure to check for
ground and voltage to the integrated control.
1 -
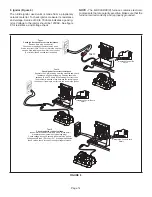
Measure the AC voltage between Line Neutral
(spade terminals) and “C” terminal (low voltage
terminal block) on the integrated control. See figure
20. A wide variation in the voltage between Line
Neutral and “C” as a function of load indicates a
poor or partial ground. Compare the readings to the
table below. If the readings exceed the maximum
shown in table 14, make repairs before operating
the furnace.
2 - In addition, measure the AC voltage from Line Hot
to Line Neutral (spade terminals) on the integrated
control. See figure 21. This voltage should be in the
range of 97 to 132 Vac.
NOTE -
Figures 21 and 22 are typical ignition control
illustrations.
CHECK VOLTAGE BETWEEN LINE NEUTRAL
AND LOW VOLTAGE “C” TERMINAL
FIGURE 20
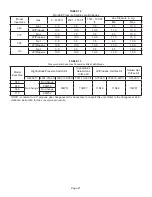
TABLE 14
Furnace Status
Measurement VAC
Expected
Maximum
Power on Furnace Idle
0.3
2
CAI/Ignitor Energized
0.75
5
Indoor Blower Energized
Less than 2
10
CHECK VOLTAGE BETWEEN LINE HOT
AND LINE NEUTRAL
FIGURE 21
V-TYPICAL OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
A-Blower Operation and Adjustment
NOTE-
The following is a generalized procedure and does
not apply to all thermostat controls.
1 -
Blower operation is dependent on thermostat control
system.
2 - Generally, blower operation is set at thermostat
subbase fan switch. wWith fan switch in ON position,
blower operates continuously. With fan switch in
AUTO position, blower cycles with demand or runs
continuously while heating or cooling circuit cycles.
3 - Depending on the type of indoor thermostat, blower
and entire unit will be off when the system switch is
in OFF position.