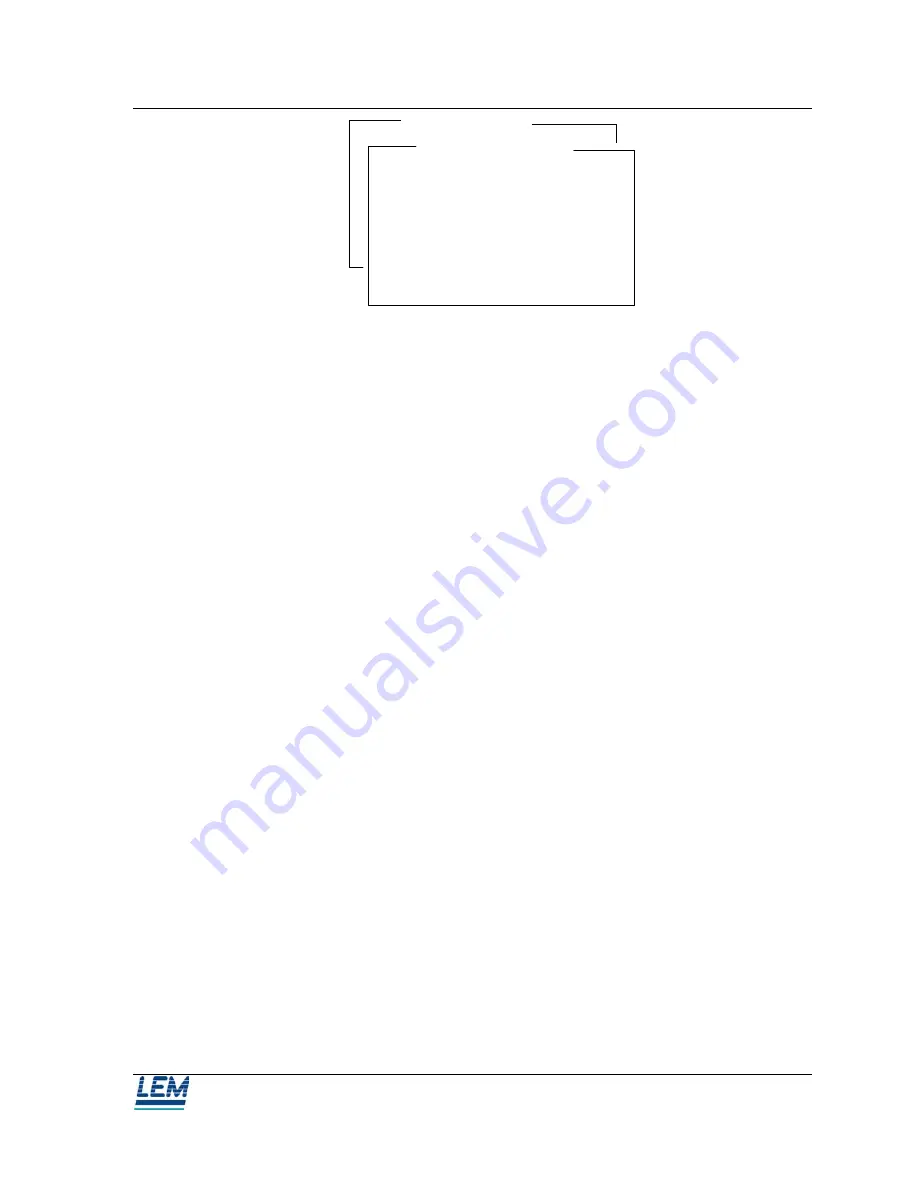
Primary Training
Calibration
AC Gain correction
Input the value of the AC voltage
connected to the analog input (s)
number : 1
(Range is : 2 Volts RMS)
Value = 1 Volts RMS
OK to calibrate input
Offset correction
Apply to the input the same voltage as entered on the screen, then move the cursor to
the [OK] icon, and press [ENTER]. The software starts the gain adjustment. As for
the offset, this adjustment can be unsuccessful, and will be indicated by an error
message appearing on the screen.
The error of gain adjustment can be due to the application of a voltage that does not
correspond to the voltage introduced on the screen, or to a wrong input range
adjustment, a mis-placed jumper on the 424 isolation cards, or an unstable AC
calibration source.
3.3.4 Notes
When an input range is changed on the isolation card, the calibration process must be
completed again.
For better precision, the reference source (voltage or current) used during calibration,
must be between 50% and 100% of the selected range, except for high current ranges,
see further.
The low value resistor shunts (for example 0.1
Ω
, 0.47
Ω
,...) are not able to withstand
the maximum current continuously (see shunt specifications, SENS 224-xx).
Therefore, it is highly recommended to calibrate such inputs with the nominal current
values, i.e. 5 to 10 amps RMS for 0.1
Ω
shunts, and 1 to 5 amps RMS for 0.47
Ω
shunts. This way, the power dissipation will be the same during calibration as during
normal use, canceling gain drift due to temperature variation of the shunt.
When DC calibration mode is used, the polarity of the reference signal must be
respected. Only positive signals are used. Terminals numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,6 7 and 8
are the positive input wires; terminals numbered 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18
are the negative input wires.
When AC calibration mode is used, the reference signal must be a sine-wave, with a
frequency of 50Hz +/- 0.1Hz when 50Hz mode is selected, and 60Hz +/- 0.1Hz when
60Hz mode is selected.
9200-14 REV E
Page 15
















































