LT-400CL
19
6.3.10 Shading correction
Shading is caused either by illumination with uneven distribution of light across the
surface, or by reductions in the light transmission ratio towards the edges of a lens.
The shading correction incorporated in the camera will compensate for this effect by as
much as 20% of the brightest signal.
Shading is not compensated for each individual pixel. The signal is averaged across groups
of 8 pixels in relation to the whole line. The pixel response non-uniformity will be
superimposed on the output also after shading correction has been performed. Therefore,
it is recommended to perform PRNU correction before shading correction.
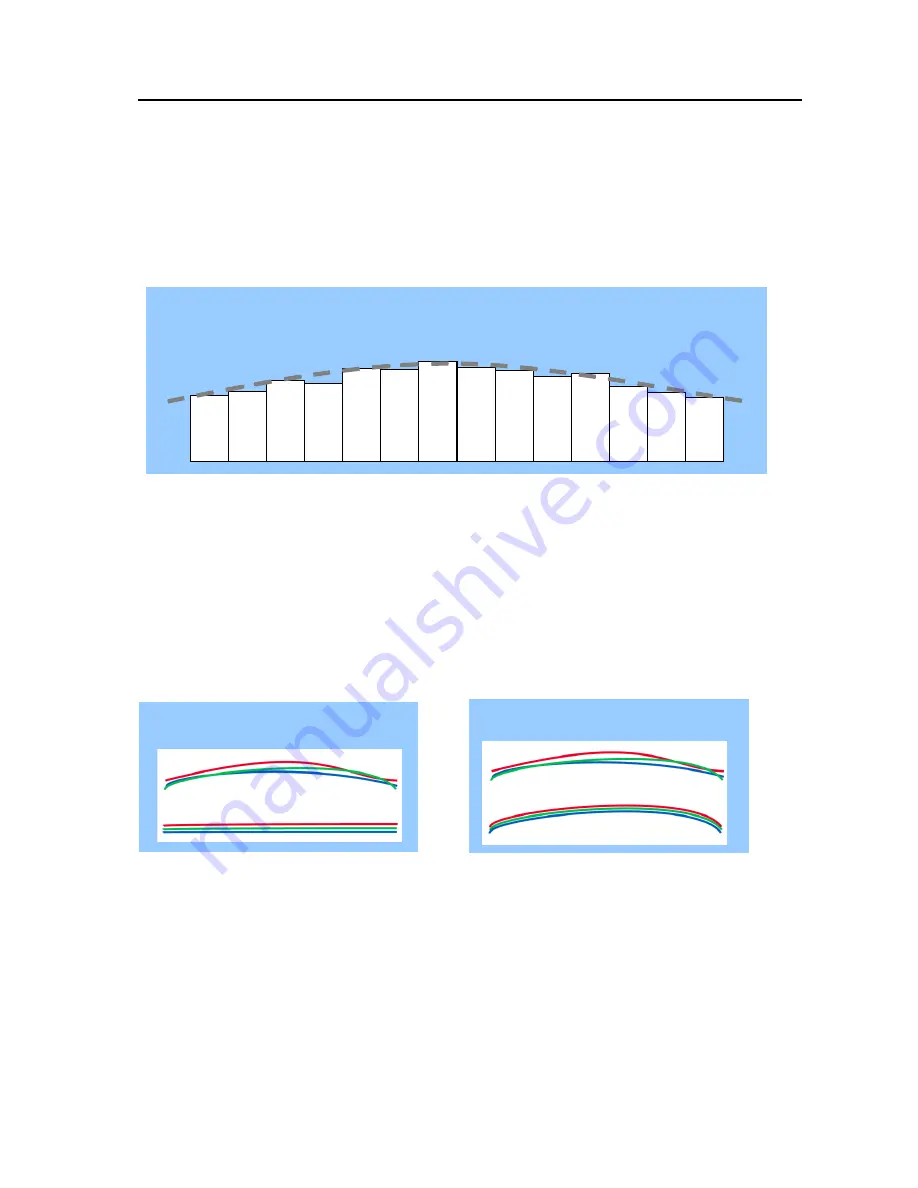
Fig.20 Shading correction
The shading correction has two ways to compensate, flat shading correction and color
shading correction.
Flat shading correction compensates red, blue and green signals to be flat output. The
range of compensation is within plus-or-minus 20% as compared the brightest signal level.
It may not compensate enough according to the lenses and/or lighting in use.
Color shading correction compensates red and blue signals to match with green signal
characteristics.
The following drawings show the concepts for flat and color shading corrections.
Fig.21 Flat shading correction Fig.22 Color shading correction
Shading caused by uneven illumination or transmission at the edges of the lens.
Pixel response non-uniformity will be superimposed on the output signal
Individual shading correction
per channel
Shading correction tracking
the green channel
















































