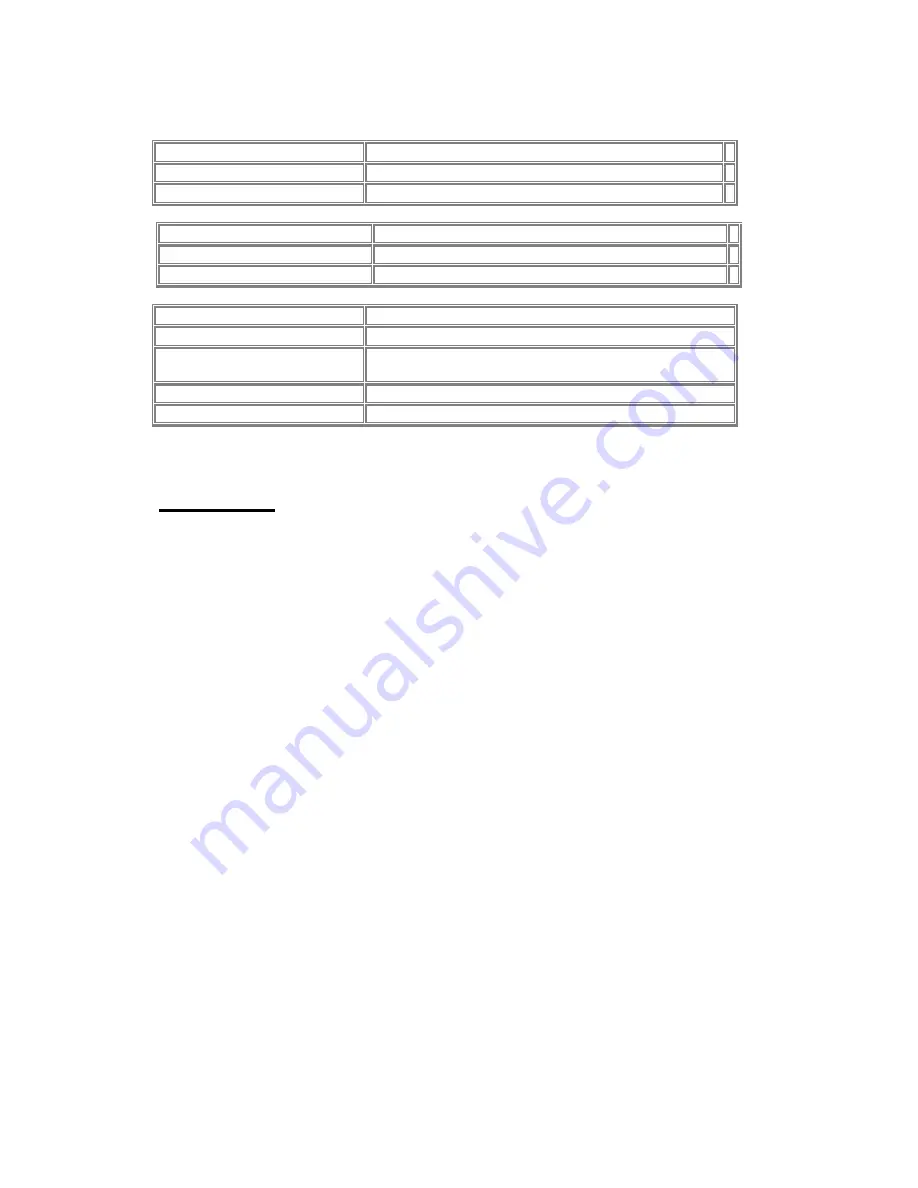
Standby
135 mW
Sleep
45 mW
Voltage 3.3
V
Operating Systems
Windows* XP, 2000, 98, 98SE, Me, NT 4.0
WECA
WiFi certification for 802.11b
WHQL Yes
WLAN Standard
IEEE 802.11b
Architecture
Infrastructure or ad hoc (peer-to-peer)
Roaming
802.11b compliant for seamless roaming between
respective access points (802.11b)
Security
LEAP, TKIP, 802.1x, EAP-TLS, 128-bit and 64-bit WEP
Product Safety
UL, C-UL, CB (IEC 60590)
9.Glossary
Numerical
802.11 x:
A series of IEEE specifications for LANs: currently 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11g.
Using any one of these extensions to the 802.11 standard permits wireless communication
between a client and an access point or between two clients. The various specifications govern
transmission speeds and radio frequencies as well as fall-back rates and other characteristics.
The upcoming standard 802.11i will provide additional security specific to WLANs, and 802.11e
will address quality of service.
A
Access Point:
A device that serves as a communications hub for wireless clients and provides
a connection to a wired LAN.
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES):
A federal information-processing standard, supporting
128-, 192-, and 256-bit keys.
B
Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID):
A unique identifier for each wireless client on a wireless
network. The BSSID is the Ethernet MAC address of each adapter on the network.
Bit Rate:
The total number of bits (ones and zeros) per second that a network connection can
support. Note that this bit rate will vary, under software control, with different signal path
conditions.
Bluetooth:
An incompatible, very short-range lower speed communications system (PAN),
developed first in Europe as a “cable replacement” for printers and similar peripheral
connections. Its usage has expanded to include cordless earphones and similar devices. It uses
the 2.4 GHz ISM band, and “co-exists” with 802.11b. Here the term, “co-exist” means that not all
researchers agree on the amount of mutual interference generated when both systems operate
in the same location.
Broadcast SSID:
Used to allow an access point to respond to clients on a wireless network by
sending probes.
D
Data Rate (Information Rate):
Not all bits carry user information. Each group (packet) of bits
contains headers, trailers, echo control, destination information, and other data required by the
transmission protocol. It is important to understand the difference between bit rate and data rate,
Содержание WM3B2100
Страница 45: ......









































