Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
Intel® Quark™ SE Microcontroller C1000
Platform Design Guide
June 2017
28
Document Number: 334715-004EN
5.0
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
The Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) block allows individual control of the frequency
and duty cycle of four output signals. The PWM block also supports use as a Timer
block for the purposes of generating periodic interrupts. A possible usage model
includes connecting PWM to drive a haptic driver. The four PWM pins are also
multiplexed and can be used as a GPIO. Four 32-bit timers running at system clock
can be configured to generate four PWM outputs.
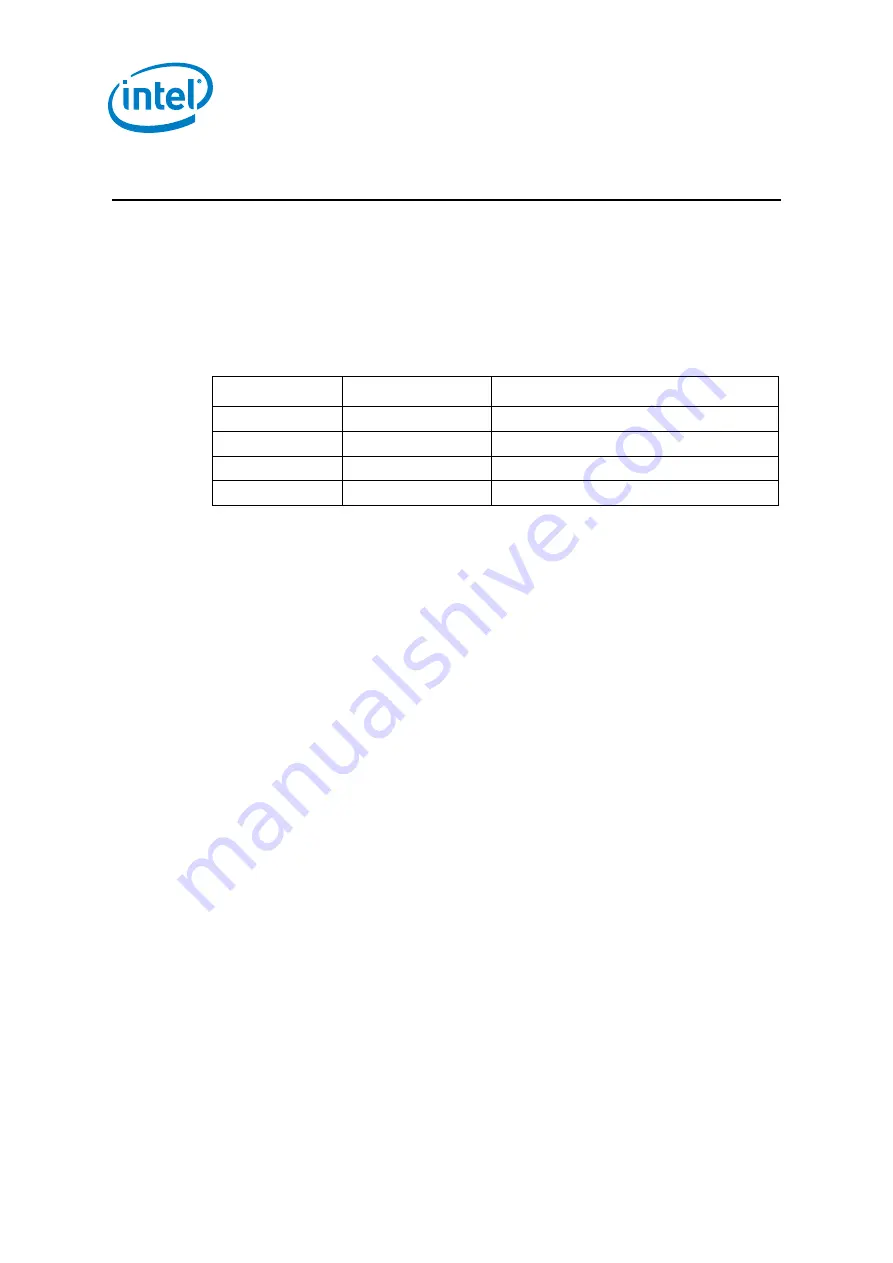
Table 9. PWM Interface Signals
Signal Name
Direction/ Type
Description
PWM[0]
Output
PWM output 0
PWM[1]
Output
PWM output 1
PWM[2]
Output
PWM output 2
PWM[3]
Output
PWM output 3
The following is a list of PWM features:
Four counters capable of operating in PWM Mode or Timer Mode
PWM Mode
Configurable high and low times for each PWM Output
−
Minimum high and low time of 2 32MHz clock periods (8MHz)
−
Maximum high and low time of 2^32 32MHz clock periods (< 1Hz)
High and low time granularity of a single 32MHz clock period
Interrupt generation always on both the rising and falling edges of the PWM
Output
Interrupt control per PWM Output
−
Interrupt generation only on both edges of the PWM Output
−
Interrupt mask capability
Timer Mode
32-bit timer operating at 32MHz
−
Timer periods from 1 32MHz clock period (31.25ns) to 2^32-1
−
32MHz clock periods (134s)
Interrupt control per timer:
−
Interrupt generation on timer expiry
−
Interrupt mask capability
5.1
PWM Signaling
The Timer and PWM block supports the generation of PWM Output signals with
configurable low and high times, which allows both the duty cycle and frequency to
be set.
Example PWM Output signals are shown in the following figures.






























