I2C Interface
Intel® Quark™ SE Microcontroller C1000
June 2017
Platform Design Guide
Document Number: 334715-004EN
27
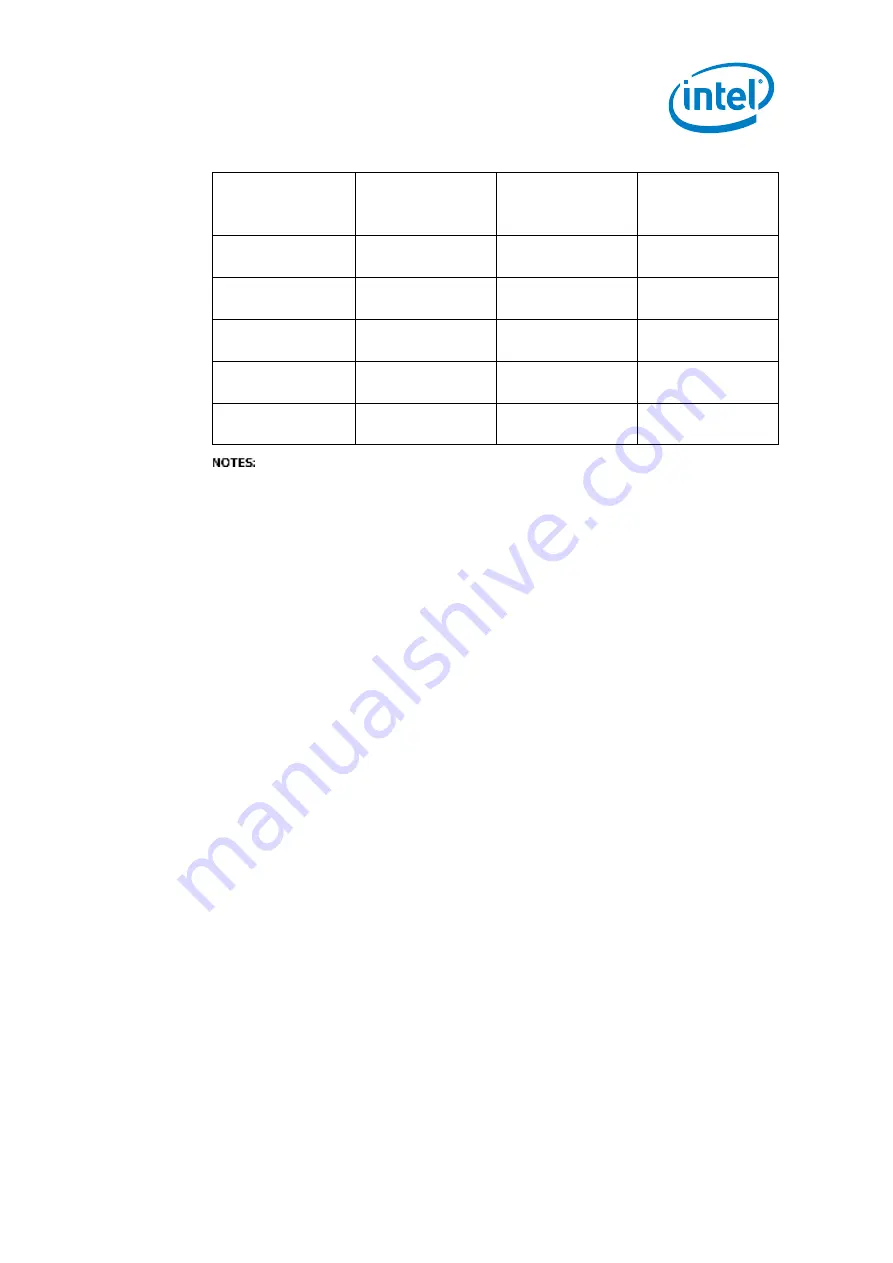
Table 8. Capacitance Estimates for Calculating Rpu Values
Capacitance
Pull-up range
100 kHz
Pull-up range
400 kHz
Pull-up range
1000 kHz
10 pF to 40 pF
1.1 kΩ to 9.0 kΩ
2.2 kΩ
1.0 kΩ to 1.2 kΩ
40 pF to 100 pF
1.2 kΩ to 7.2 kΩ
0.6 kΩ to 2.6 kΩ
750 Ω
100 pF to 200 pF
1.2 kΩ to 4.0 kΩ
0.6 kΩ to 1.3 kΩ
500 Ω
200 pF to 300 pF
1.2 kΩ to 2.6 kΩ
0.6 kΩ to 0.9 kΩ
320 Ω
300 pF to 400 pF
1.2 kΩ to 2.0 kΩ
0.6 kΩ
240 Ω
1.
Length matching between Data and Clk is 540 mils.
2.
Cap per inch of board (pF) = 3 pF/inch (for the current stackup).
3.
If the nominal trace width is not possible in the breakout area, use 4 mils as the minimum
trace width. Choose a stackup so that 50 Ohms will be minimum 4 mils.
4.
It is best to meet nominal impedance and spacing requirement at breakout region. If not, you
must meet at least the minimum requirement.
General Design Considerations:
System designers must consider the total bus capacitance, which includes both SoC
and device pin capacitance, and board trace length capacitance as well. The number
and types of I
2
C devices on each I
2
C bus must be determined, not exceeding the
maximum bus capacitive load of 400 pF for each I
2
C bus. While choosing the pull-
up resistor, it is important to remember that it must not be made so large that the
bus time constant (Resistance X Capacitance) does not meet the I
2
C rise and fall
time specification. Analysis of a particular layout is required to confirm correct
operation.
§






























