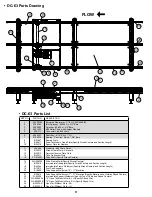
5
Ambient Temperature
Degrees F
SAE
ISO
20-40
40-100
100-120
20
30
40
46 or 68
100
150
CAUTION!
Because of the many moving parts on the conveyor, all personnel in the
area of the conveyor need to be warned that the conveyor is about to be started.
WARNING!
Electrical controls shall be installed and wired by a qualified electrician. Wiring
information for the motor and controls are furnished by the equipment manufacturer.
• Electrical Equipment
CONTROLS
Electrical Code: All motor controls and wiring shall conform to the National
Electrical Code (Article 670 or other applicable articles) as published by the
National Fire Protection Association and as approved by the American Standards
Institute, Inc.
CONTROL STATIONS
A) Control stations should be so arranged and located that the operation of the
equipment is visible from them, and shall be clearly marked or labeled to indicate
the function controlled.
B) A conveyor which would cause injury when started shall not be started until
employees in the area are alerted by a signal or by a designated person that the
conveyor is about to start.
When a conveyor would cause injury when started and is automatically
controlled or must be controlled from a remote location, an audible device shall
be provided which can be clearly heard at all points along the conveyor where
personnel may be present. The warning device shall be actuated by the controller
device starting the conveyor and shall continue for a required period of time
before the conveyor starts. A flashing light or similar visual warning may be used
in conjunction with or in place of the audible device if more effective in particular
circumstances.
Where system function would be seriously hindered or adversely affected by
the required time delay or where the intent of the warning may be misinterpreted
(i.e., a work area with many different conveyors and allied devices), clear, concise,
and legible warning shall be provided. The warning shall indicate that conveyors
and allied equipment may be started at any time, that danger exists, and that
personnel must keep clear. The warnings shall be provided along the conveyor at
areas not guarded by position or location.
C) Remotely and automatically controlled conveyors, and conveyors where
operator stations are not manned or are beyond voice and visual contact from drive
areas, loading areas, transfer points, and other potentially hazardous locations on
the conveyor path not guarded by location, position, or guards, shall be furnished
with emergency stop buttons, pull cords, limit switches, or similar emergency stop
devices.
All such emergency stop devices shall be easily identifiable in the immediate
vicinity of such locations unless guarded by location, position, or guards. Where
the design, function, and operation of such conveyor clearly is not hazardous to
personnel, an emergency stop device is not required.
The emergency stop device shall act directly on the control of the conveyor
concerned and shall not depend on the stopping of any other equipment. The
emergency stop devices shall be installed so that they cannot be overridden from
other locations.
D) Inactive and unused actuators, controllers, and wiring should be removed from
control stations and panel boards, together with obsolete diagrams, indicators,
control labels, and other material which serve to confuse the operator.
SAFETY DEVICES
A) All safety devices, including wiring of electrical safety devices, shall be
arranged to operate in a “Fail-Safe” manner, that is, if power failure or failure of the
device itself would occur, a hazardous condition must not result.
B) Emergency Stops and Restarts. Conveyor controls shall be so arranged
that, in case of emergency stop, manual reset or start at the location where the
emergency stop was initiated, shall be required of the conveyor(s) and associated
equipment to resume operation.
C) Before restarting a conveyor which has been stopped because of an
emergency, an inspection of the conveyor shall be made and the cause of the
stoppage determined. The starting device shall be locked out before any attempt
is made to remove the cause of stoppage, unless operation is necessary to
determine the cause or to safely remove the stoppage.
Refer to ANSI Z244.1-1982, American National Standard for Personnel Protection
– Lockout/Tagout of Energy Sources – Minimum Safety Requirements and OSHA
Standard Number 29 CFR 1910.147 “The Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/
Tagout).”
OPERATION
• Conveyor Start-Up
Before conveyor is turned on, check for foreign objects that may have been left
inside the conveyor during installation. These objects could cause serious damage
during start-up.
After conveyor has been turned on and is operating, check motors, reducers, and
moving parts to make sure they are working freely.
MAINTENANCE
• Lubrication
The drive chain is pre-lubricated from the manufacturer by a hot dipping process that
ensures total lubrication of all components. However, continued proper lubrication will
greatly extend the useful life of every drive chain.
Drive Chain lubrication serves several purposes including:
• Protecting against wear of the pin-bushing joint
• Lubricating chain-sprocket contact surfaces
• Preventing rust or corrosion
For normal operating
environments, lubricate every
2080 hours of operation or
every 6 months, whichever
comes first. Lubricate with a
good grade of non-detergent
petroleum or synthetic lubricant (i.e., Mobile 1 Synthetic). For best results, always
use a brush to generously lubricate the chain. The proper viscosity of lubricant greatly
affects its ability to flow into the internal areas of the chain. Refer to the table above
for the proper viscosity of lubricant for your application.
The drive chain’s lubrication requirement is greatly affected by the operating
conditions. For harsh conditions such as damp environments, dusty environments,
excessive speeds, or elevated temperatures, it is best to lubricate more frequently. It
may be best, under these conditions, to develop a custom lubrication schedule for your
specific application. A custom lubrication schedule may be developed by inspecting the
drive chain on regular time intervals for sufficient lubrication. Once the time interval is
determined at which the chain is not sufficiently lubricated, lubricate it and schedule the
future lubrication intervals accordingly.
• Trouble Shooting
The following chart list possible problems that may occur in the operation of a powered conveyor.
TROUBLE SHOOTING DRIVES
TROUBLE
CAUSE
SOLUTION
Conveyor will not start or
motor quits frequently.
1) Motor is overloaded or is drawing too much current.
1) Check for overloading of conveyor.
2) Check heater or circuit breaker and change if necessary.
Drag chain and sprockets
wear excessively.
1) Lack of lubrication on chain may have caused chain to
stretch and create an improper chain to sprocket mesh.
2) Sprockets are out of alignment.
3) Loose chain.
1) Replace chain and sprockets. NOTE: If problem reoccurs, a chain take-up may be
required.
2) Align drive sprockets with fixed idlers.
3) Tighten chain.
Loud popping or grinding
noise.
1) Defective bearing.
2) Loose set screws in bearing.
3) Loose drive chain.
1) Replace bearing.
2) Tighten set screw.
3) Tighten chain.
Motor or reducer
overheating.
1) Conveyor is overloaded.
2) Low voltage to motor.
3) Low lubricant level in reducer.
1) Check capacity of conveyor and reduce load to recommended level.
2) Have electrician check and correct as necessary.
3) Relubricate per manufacturer’s recommendations. For HYTROL reducer, refer to
separate manual.
Содержание DC62
Страница 15: ...15 ...