Pub. 42004-501C
Division 2 VoIP Telephones
—Wired and WiFi
Page 20 of 22
P:\Standard IOMs - Current Release\42004 Instr. Manuals\42004-501C.docx
03/20
Troubleshooting
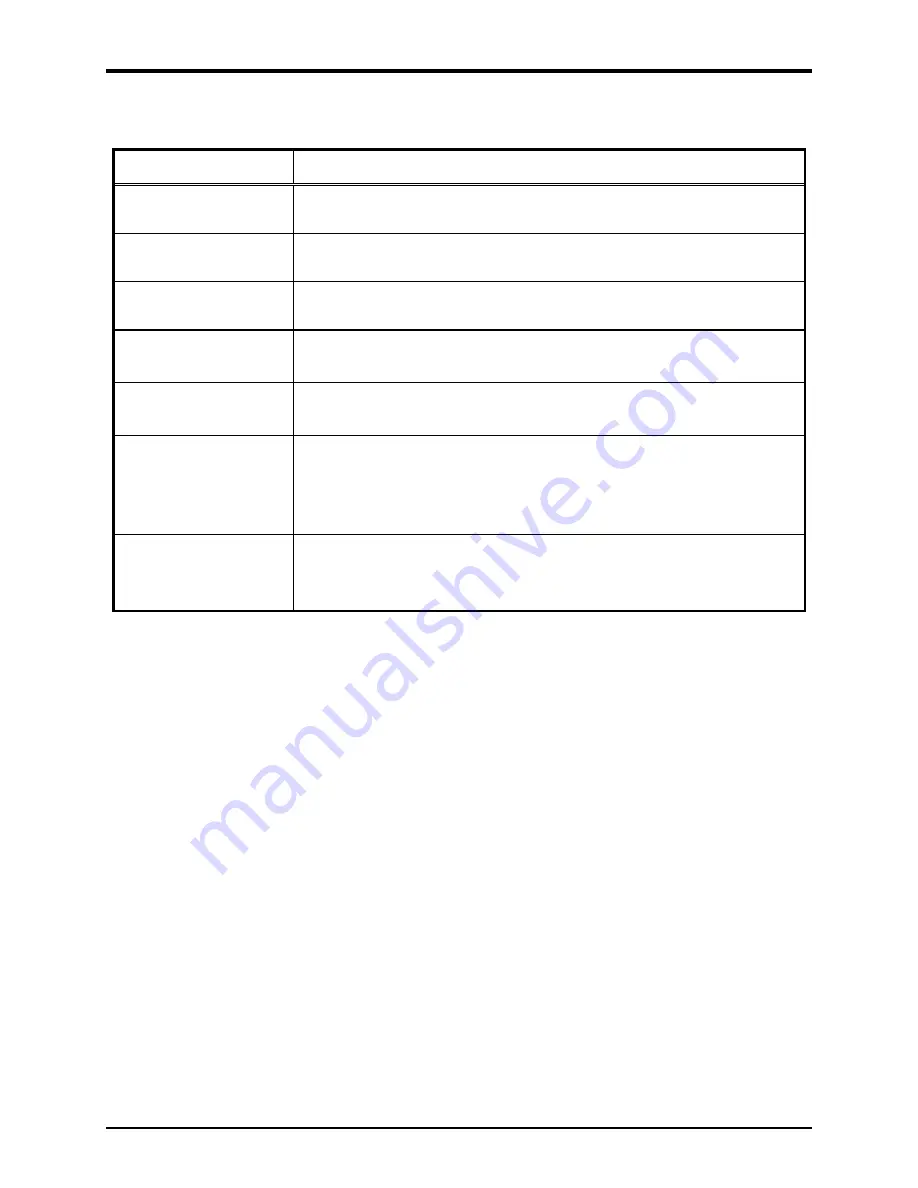
Table 6. Troubleshooting Chart
Problem
Possible Solution
low volume in handset
or headset
Increase the volume setting using the Volume Adjust button on the front
panel.
high volume in handset
or headset
Decrease the volume setting using the Volume Adjust button on the front
panel.
front panel push buttons
are not operational
Verify the push buttons are properly configured.
inputs not operational
Check the input connections.
Verify the inputs are properly configured.
outputs not operational
Check the output connections.
Verify the outputs are properly configured.
cannot make or receive
calls
Check the connection of the LAN cable.
Verify that power is applied to the unit.
Verify the LAN parameters have been configured properly.
Verify the telephone has been set up on the network.
no power indication
Check the power connections.
Check fuses. Replace fuses with identical type/ratings.
If using POE, check the operation of the POE equipment.
Monitoring and Reporting
Each telephone can recognize and generate several hardware and configuration fault condition alarms.
These alarms can be signaled to a remote site using three methods:
•
syslog output over TCP
•
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
•
TMA (Telephone Management Application) software (purchased separately)
Available alarms are:
•
handset integrity loop (if applicable)
•
configuration error
•
cold reset (power cycle)
•
warm reset (internal command)
•
keypad error, such as a stuck button (if applicable)
•
key hook (off-hook status, if applicable)
•
register fail
•
audio path test (speaker/microphone test)



































