58
•
To configure an area as a totally stub area, the
stub
command must be configured on routers in the
area, and the ABR of the area must be configured with the
stub
[
no-summary
] command.
•
A totally stub area cannot have an ASBR because AS external routes cannot be distributed into the
stub area.
•
Virtual links cannot transit totally stub areas.
NSSA area
Similar to a stub area, an NSSA area does not import AS external LSAs (Type-5 LSAs), but can import
Type-7 LSAs generated by the NSSA ASBR. The NSSA ABR translates Type-7 LSAs into Type-5 LSAs and
advertises the Type-5 LSAs to other areas.
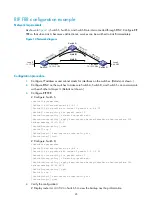
In the following figure, the OSPF AS contains Area 1, Area 2, and Area 0. The other two ASs run RIP.
Area 1 is an NSSA area. The ASBR redistributes RIP routes in Type-7 LSAs into Area 1. Upon receiving
these Type-7 LSAs, the NSSA ABR translates them to Type-5 LSAs, and then advertises the Type-5 LSAs to
Area 0.
The ASBR of Area 2 redistributes RIP routes in Type-5 LSAs into the OSPF routing domain. However, Area
1 does not receive these Type-5 LSAs because it is an NSSA area.
Virtual links cannot transit NSSA areas.
Figure 20
NSSA area
Comparison between the areas
Figure 21
Comparison between the areas
shows the comparison of the areas:
•
In a totally stub area, the ABR distributes a Type 3 default route, rather than external routes and
inter-area routes.
•
A stub area can import inter-area routes, but a stub area cannot.
Totally Stub
area
Stub area
NSSA area
Totally NSSA
area
Permits
Type 3 LSAs
Permits
Type 7 LSAs
within the area
Does not
permit Type 3
LSAs
A Type 3 default route
can be distributed in the
area, while Type 3 and
Type 5 LSAs cannot be
distributed in the area