122
NextHop: 13.13.13.2 Interface: Vlan-interface200
BkNextHop: 12.12.12.2 BkInterface: Vlan-interface100
RelyNextHop: 0.0.0.0 Neighbor : 0.0.0.0
Tunnel ID: 0x0 Label: NULL
BKTunnel ID: 0x0 BKLabel: NULL
State: Active Adv Age: 00h01m27s
Tag: 0
# Display route 1.1.1.1/32 on Switch D to view the backup next hop information.
[SwitchD] display ip routing-table 1.1.1.1 verbose
Routing Table : Public
Summary Count : 1
Destination: 1.1.1.1/32
Protocol: OSPF Process ID: 1
Preference: 10 Cost: 1
IpPrecedence: QosLcId:
NextHop: 13.13.13.1 Interface: Vlan-interface200
BkNextHop: 24.24.24.2 BkInterface: Vlan-interface101
RelyNextHop: 0.0.0.0 Neighbor : 0.0.0.0
Tunnel ID: 0x0 Label: NULL
BKTunnel ID: 0x0 BKLabel: NULL
State: Active Adv Age: 00h01m27s
Tag: 0
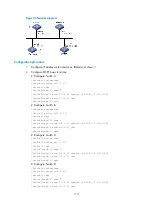
Configuring BFD for OSPF
Network requirements
As shown in
, OSPF is enabled on Switch A, Switch B and Switch C that are reachable to each
other at the network layer.
After the link over which Switch A and Switch B communicate through a Layer 2 switch fails, BFD can
quickly detect the failure and notify OSPF of the failure. Switch A and Switch B then communicate through
Switch C.
Figure 48
Network diagram
Device Interface IP
address
Device
Interface
IP address
Switch A
Vlan-int10
10.1.0.102/24
Switch B
Vlan-int10
10.1.0.100/24
Vlan-int11
11.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int13 13.1.1.1/24