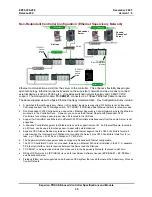
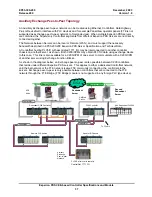
EP03-300-200
December,
2003
Release 200
Version 1.0
Experion PKS CEE-based Controller Specifications and Models
29
C200 Control Processor Processing and Memory Resources
The
C200 Control Processor
provides a flexible execution environment for performing a variety of
control tasks at different execution speeds. To determine how much control a Processor can perform,
Processor Usage
and
Memory Usage
must be considered. Available CPU and memory resources
determine the number of modules or blocks a C200 Control Processor can execute. Other constraints,
such as total number of CMs and SCMs, must also be taken into account.
These specifications should be reviewed to ensure that Experion PKS meets the application
requirements.
The table below represents an example of non-redundant Control processor configuration
(not necessarily typical).
C200 Control Processor (Non-Redundant, 50 msec CEE) Capacity, Sample Configuration
Module Type
No. of
Modules
Period,
sec
Module
PU
Module
MU
Total PUs*
Total
MUs
I/O Module (64 max)
40 0.05
0.3 0.6
240
24
Analog Data Acquisition CM
20 1
2.9 7.4
58 148
Small Analog Data Acq. CM
10 2
0.47 1.0
2.35
10
Regulatory Control CM
100 0.5
2.8 3.9
560 390
Auxiliary Function CM
10 0.5
4.2 13.1
84
131
Digital Data Acquisition CM
20 0.1
1.2 3.1
240
62
Small Digital Data Acq. CM
10 0.1
0.22 0.6
22
6
Device Control CM
140 0.1
1.3 3.1
1820 434
Logic Control CM
10 0.1
1.0 3.5
100
35
Sequential Control Module (SCM)
50 1
2.0 55
100 2750
Total 3226
3990
Max 3600/1600**
4000
PU = Processing Unit per Control Cycle; MU = Memory Unit, Kbytes
PUs for any given CM = (PU per Cycle) / (Cycle Time, sec.)
*Total PUs = (No. of Modules) x (Module PU) / (Period, sec.) for each CM type.
Available Period for all CM and SCM types are 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 sec. I/O Modules fixed at 0.05 sec.
**Total PUs for Non-Redundant/Redundant C200 Control Processors (Module PUs provided above apply to a non-
redundant controller, see table 17 for Module PU values for redundant controllers).