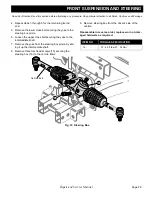
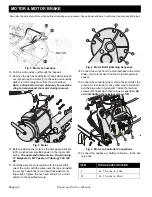
Page H-2
BATTERIES & CHARGING
Repair and Service Manual
Read all of Section B and this section before attempting any procedure. Pay particular attention to all Notes, Cautions and Warnings.
B
Always wear a safety
shield or approved
safety goggles when
adding water or
charging batteries.
Any electrolyte spills
should be neutralized with a solution of 1/4
cup (60 ml) sodium bicarbonate (baking
soda) dissolved in 1 1/2 gallons (6 liters) of
water and flushed with water.
Overfilling batteries may result in electro-
lyte being spilled from the battery during
the charge cycle. Expelled electrolyte may
cause damage to the vehicle and storage
facility.
Aerosol containers of battery terminal pro-
tectant must be used with extreme care.
Insulate metal container to prevent can
from contacting battery terminals which
could result in an explosion.
Wrap wrenches with vinyl
tape to prevent the possi-
bility of a dropped wrench
from ’shorting out’ a bat-
tery, which could result in
an explosion and severe personal injury or
death.
BATTERY
A battery is defined as two dissimilar metals immersed
in an acid solution. If the acid is absent or if the metals
are not dissimilar, a battery has not been created. The
batteries most commonly used in these vehicles are
lead acid.
A battery does not store electricity, but is able to pro-
duce electricity as the result of a chemical reaction
which releases stored chemical energy in the form of
electrical energy. The chemical reaction takes place
faster in warm conditions and slower in cold conditions.
Temperature is important when conducting tests on a
battery and test results must be corrected to compen-
sate for temperature differences.
As a battery ages, it still performs adequately except
that its
capacity
is diminished. Capacity describes the
time that a battery can continue to provide its design
amperes from a full charge.
A battery has a maximum life, therefore good mainte-
nance is designed to maximize the
available
life and
reduce the factors that can reduce the life of the battery.
BATTERY MAINTENANCE
Tool List
Qty.
Insulated Wrench, 9/16"...............................................1
Battery Carrier .............................................................2
Hydrometer ..................................................................1
Battery Maintenance Kit P/N 25587-G01.....................1
At Each Charging Cycle
Before charging the batteries, inspect the plug of the
battery charger and vehicle receptacle housing for dirt
or debris.
Charge the batteries after each days use.
Monthly
•
Inspect all wiring for fraying, loose terminations,
corrosion or deterioration of insulation.
•
Check that the electrolyte level is correct and add
suitable water as required.
•
Clean the batteries and wire terminations.
•
Coat battery terminals with commercially avail-
able protectant.
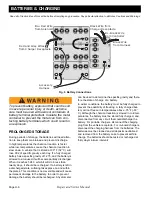
Electrolyte Level and Water
The correct level of the electrolyte is 1/2" (13 mm) above
the plates in each cell.
Fig. 2 Correct Electrolyte Level
This level will leave approximately 1/4" - 3/8" (6 - 10
mm) of space between the electrolyte and the vent tube.
Vent Cap
Gas Vent
Vent
Expansion
Space
Plates
1/2” (13 mm)
1/4” to 3/8”
(6 mm to 10mm)
Electrolyte level should be at least
1/2” (13mm) above the plates and 1/4”
to 3/8” (6 to 10 mm) below vent