3 MEMORY MAP, BUS CONTROL
3-2
EPSON
S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL
3.1 Bus Cycle
The CPU operates with CCLK as the operating clock. For CCLK, see Section 8.2, “Controlling the CPU Core
Clock (CCLK).”
The period between a CCLK rising edge and the next rising edge is assumed to be one CCLK (= one bus cycle).
As shown in Figure 3.1, the number of cycles required for one bus access depends on the peripheral or memory
module. Furthermore, the number of bus accesses depends on the CPU instruction (access size) and device size.
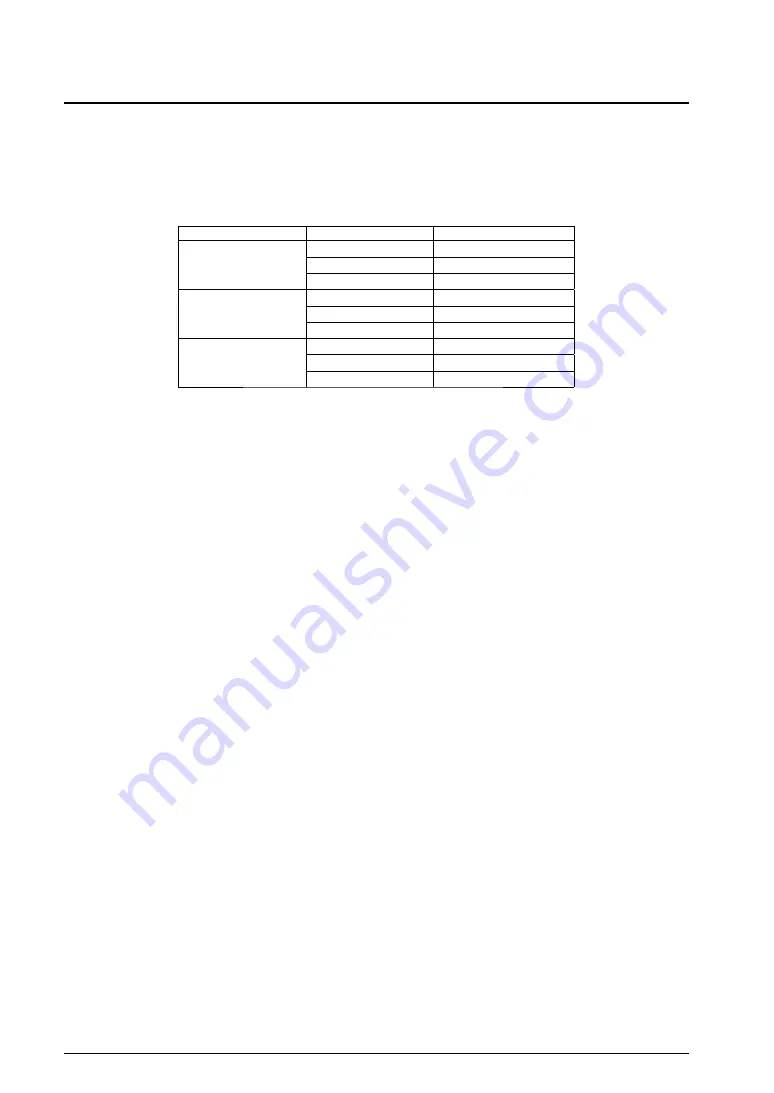
Table 3.1.1 Number of Bus Accesses
Device size
CPU access size
Number of bus accesses
8 bits
8 bits
1
16 bits
2
32 bits
*
4
16 bits
8 bits
1
16 bits
1
32 bits
*
2
32 bits
8 bits
1
16 bits
1
32 bits
*
1
∗
Handling the eight high-order bits during 32-bit accesses
During writing, the eight high-order bits are written as 0. During reading from a memory, the eight high-order
bits are ignored. However, the stack operation in an interrupt handling reads/writes 32-bit data that consists of the
PSR value as the high-order 8 bits and the return address as the low order 24 bits.
Number of bus cycles calculation example
Number of bus cycles when the CPU accesses the display RAM area (eight-bit device, set to two access cycles)
by a 16-bit read or write instruction.
2
[cycles]
×
2 [bus accesses] = 4 [CCLK cycles]
3.1.1 Restrictions on Access Size
The modules shown below have a restriction on the access size. Appropriate instructions should be used in
programming.
Flash memory
The Flash memory allows only 16-bit write instructions for programming. Reading data from the Flash memory
has no such restriction.
SPI, I
2
C
The SPI and I
2
C registers allow only 16-bit read/write instructions for accessing.
Other modules can be accessed with an 8-bit, 16-bit, or 32-bit instruction. However, reading for an unnecessary
register may change the peripheral module status and it may cause a problem. Therefore, use the appropriate
instructions according to the device size.
3.1.2 Restrictions on Instruction Execution Cycles
An instruction fetch and a data access are not performed simultaneously under one of the conditions listed below.
This prolongs the instruction fetch cycle for the number of data area access cycles.
• When the S1C17704 executes the instruction stored in the Flash area and accesses data in the Flash area, display
RAM area or internal peripheral area 2 (0x5000–)
• When the S1C17704 executes the instruction stored in the internal RAM area and accesses data in the internal
RAM area
Содержание S1C17704
Страница 1: ...TECHNICAL MANUAL S1C17704 CMOS 16 BIT SINGLE CHIP MICROCOMPUTER ...
Страница 22: ...1 OVERVIEW 1 10 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 42: ...3 MEMORY MAP BUS CONTROL 3 12 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 82: ...6 INTERRUPT CONTROLLER ITC 6 26 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 108: ...8 CLOCK GENERATOR CLG 8 8 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 112: ...9 PRESCALER PSC 9 4 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 138: ...10 I O PORTS P 10 26 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 156: ...11 16 BIT TIMERS T16 11 18 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 208: ...14 8 BIT OSC1 TIMER T8OSC1 14 16 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 234: ...16 STOPWATCH TIMER SWT 16 14 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 242: ...17 WATCHDOG TIMER WDT 17 8 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 264: ...18 UART 18 22 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 300: ...20 I2C 20 20 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 320: ...21 REMOTE CONTROLLER REMC 21 20 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 360: ...24 ON CHIP DEBUGGER DBG 24 6 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
Страница 362: ...25 BASIC EXTERNAL WIRING DIAGRAM 25 2 EPSON S1C17704 TECHNICAL MANUAL THIS PAGE IS BLANK ...
















































