Chapter 4
Configuration
MAN_905G_1.16
Page 66
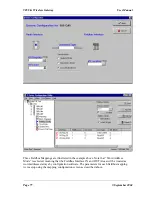
command is a “Digital” write, meaning that the register values will be written as
digital/binary values”.
If the Modbus Slave device does not respond to the Modbus command, the 905G will try
another 3 times (“Max Retries” = 3). The Modbus command will be sent to the Modbus
Slave every 100msec. The address of the Modbus Slave is 1 (permissible addresses are 1 –
255). Because a digital write command has been selected, the destination register type will
be digital outputs, with Modbus tag “0xxxxx”. The first destination Modbus location is 12
(or 00012) - as there are 6 registers transferred, the destination locations will be 00012 –
00017.
The second example is a register read command to the same Modbus Slave (address 1). The
command requests the Modbus Slave to return the values of 10 registers which will be stored
in I/O registers 463 - 473 in the 905G. As the command is a “register read” command, the
target Modbus locations will be of the type 3xxxx. The starting location is 30001. So the
values of locations 30001 – 30010 in Modbus Slave 1 will be transferred to I/O registers 463
– 473 in the 905G.
The CF Register (“comms fail” register) acts as a digital alarm – the value of the register will
normally be 0, and will be set to FFFF (hex) if the slave device does not positively respond to
the serial command within
Max Retries
attempts. In the examples, the same CF Register
(4327 – i.e. DOT8) has been used for both serial mappings, such that the local digital output
will be activated if the slave fails to respond to either serial command. Alternately, any other
internal register could have been chosen and mapped via radio if desired.