905U-G Wireless Gateway
User Manual
Page 115
©September 2004
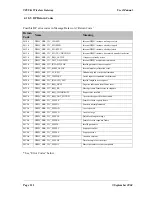
An IP Address is divided into two main parts
subnet
ID and
host
ID. All devices on the same
local network must have the same subnet ID, but a unique host ID. To separate these two
parts a
subnet mask
is used. In its simplest form, the subnet mask is a four byte pattern where
a value of 255 allocates the corresponding byte of the IP Address to the subnet ID, and a
value of 0 allocates the corresponding byte of the IP Address to the host ID.
For example, a common subnet mask is shown in the example below. Looking at the IP
Address located directly above the Subnet Mask in this example, it can be seen that the IP
Address values directly above a subnet mask value of 255 correspond to the subnet ID.
Conversely, the IP Address values directly above a subnet mask value of 0 correspond to the
host ID. So, in this example, the subnet ID is 169.254.100 and the host ID is 175.
Special case IP addresses
Devices on an Ethernet network are not allowed to be configured to the following IP
addresses; therefore do not configure the module to use any of them.
0.x.x.x - IP address where the first byte is zero
127.x.x.x - IP address where the first byte is
127
x.x.x.0 - IP address where the last byte is zero
x.x.x.255 - IP address where the last byte is
255
Gateway
The Gateway IP is the IP address of the LAN server or the host device.
Connect Timeout
The Connect Timeout parameter in the IP addressing section of the display refers to the IP
functionality of the module. If an IP connection to the module has not been active for this
amount of time, the 905G will timeout and disconnect that connection. Note that there can
be several active connections at the same time - only the inactive connection will be
disconnected.