Chapter 4
Configuration
MAN_905G_1.16
Page 114
1.
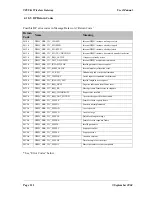
Modbus/TCP. The module supports the Modbus/TCP protocol and conforms to the
Modbus/TCP specification 1.0 (full information on this protocol can be obtained from
http://www.modicon.com/openmbus/index.html). Refer to section 4.10.2 below for
configuration details.
2.
EtherNet/IP. EtherNet/IP is based on the Allen-Bradley Control and Information
protocol, CIP, which is also the framework for both DeviceNet and ControlNet, to carry
and exchange data between nodes. Refer to section 4.10.3 below for configuration
details.
Note! The 905G only supports true EtherNet IP commands as found in A-B ControlLogix,
MicroLogix, and CompactLogix PLC’s, but does not support earlier A-B Ethernet
commands used with SLC5 PLC’s.
3.
IT-Functionality. The Ethernet 905G has several IT features, including Internet
functionality.
•
Filesystem. The module features a flexible file system with two security levels. The
size available for user files is approximately 1.4 Mbyte of non-volatile memory.
•
FTP Server. The FTP Server provides easy file management using standard FTP
clients.
•
Telnet Server. The Telnet server features a command line interface similar to the MS-
DOS™ environment.
•
HTTP Server. The module features a flexible HTTP server with SSI functionality.
This enables the user to configure a web interface (or web page) accessing I/O values
in the 905G.
•
Email Client (SMTP). Predefined messages stored within the file system can be sent,
triggered by a specified I/O value in the 905G. It is also possible to include I/O values
in emails, using SSI functionality.
•
IP Access Control. It is possible to configure which IP addresses and what protocols
that are allowed to connect to the module.
For further details, refer to Appendix 2.
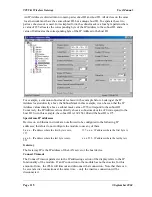
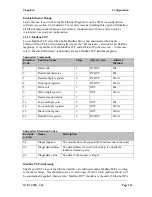
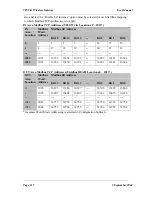
4.11.1
Setting IP Address
The Ethernet IP address can be set from the configuration software or via the Ethernet port or
via the selector switches in the top end-plate of the module. If the “Enable Switch Address”
box is not selected, then the address entered in the program will be used and the switch value
ignored. The IP address can be overwritten from the Ethernet port. If the “Enable Switch
Address” box is selected, then the address entered in the configuration program will be
ignored and the rotary switch read on start-up of the 905G.
The IP address is used to identify each node on the Ethernet network. Therefore, each node
on the network must have a unique IP address. IP addresses are written as four decimal
integers (0-255) separated by periods, where each integer represents the binary value of one
byte in the IP address. This is called dotted-decimal notation. Example: 169.254.100.175
Subnet Mask