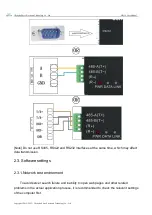
Chengdu Ebyte Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.
NB114 User Manual
Copyright ©2012–2023
,
Chengdu Ebyte Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.
4. Product function
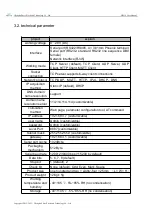
4.1. Network parameters
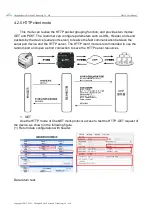
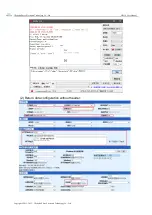
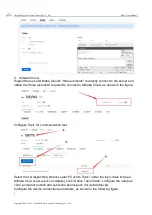
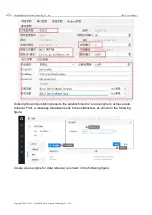
4.1.1.IP address type
The IP address is the identification of the module in the LAN, which is unique in the LAN.
Therefore, it cannot be duplicated with other devices in the same LAN. The IP address of the
module can be obtained by static IP and DHCP.
(
1
)
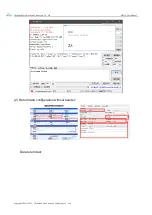
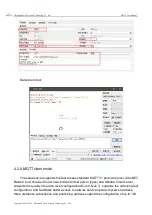
Static IP: The static IP needs to be set manually by the user. In the process of setting,
pay attention to writing the IP, subnet mask and gateway at the same time. The static IP
is suitable for the scenario where the IP and device need to be counted and
corresponding one by one.
Advantages: access to devices that cannot be assigned IP addresses can be searched
through the full-segment broadcast mode, which is convenient for unified management;
Disadvantages: Different intranet segments in different LANs lead to the failure of
normal TCP/UDP communication.
(
2
)
Dynamic DHCP: DHCP is mainly used to dynamically obtain IP address, gateway
address, DNS server address and other information from the gateway host, thus
eliminating the tedious steps of setting IP address. It is applicable to scenarios where
there is no requirement for IP and no requirement for one-to-one correspondence
between IP and modules.
Advantages: The access router and other devices with DHCP server can communicate
directly, reducing the trouble of setting IP address gateway and subnet mask.
Disadvantages: If the module is connected to a network without a DHCP server, for
example, if it is directly connected to a computer, the module will not work properly.
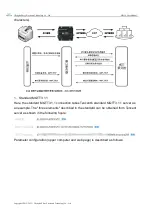
The subnet mask is mainly used to determine the network number and host number of
the IP address, indicate the number of subnets, and determine whether the module is in the
subnet.
The subnet mask must be set. Our commonly used Class C subnet mask is
255.255.255.0, the network number is the first 24 digits, the host number is the last 8 digits,