Understanding UPS Operation
5-2
Eaton 9E UPS (20–30 kVA, 208/220V) Generation 3 Installation and Operation Manual P-164000301—Rev 1
www.eaton.com/powerquality
5.2.1
Modes
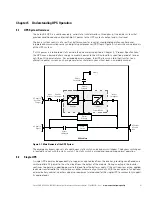
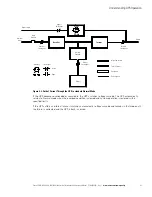
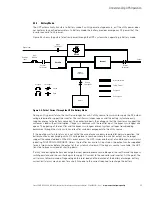
The Eaton 9EUPS supports a critical load in four different modes of operation:
l
In High-Efficiency (HE) Normal mode, commercial AC power is supplied directly to the critical load through
the internal bypass and transfers automatically to Standard Normal mode (double-conversion on demand) if
an abnormal condition is detected. HE mode is the default normal operating mode.
l
In Standard Normal mode, the critical load is supplied by the inverter, which derives its power from rectified
utility AC power. In this mode, the battery charger also provides charging current for the battery, if needed.
l
In Bypass mode, the critical load is directly supported by utility power.
l
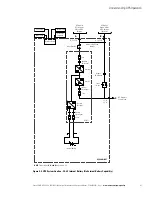
In Battery mode, the battery provides DC power, which maintains inverter operation. The battery supports
the critical load.
The following paragraphs describe the differences in the UPS operating modes, using block diagrams to show
the power flow during each mode of operation.
5.2.2
High-Efficiency Normal Mode
When the UPS is operating in HE mode, commercial AC power is supplied directly to the critical load through
the internal bypass with the power module in a standby state. If a commercial power brownout, blackout,
overvoltage, undervoltage, or out-of-tolerance frequency condition occurs the system forward transfers to
normal mode (double-conversion on demand) or battery mode. When the input line returns to normal operating
range, the UPS returns to HE operation. For charging batteries in HE mode, the UPS will revert to normal mode
to charge the batteries, then return to HE mode when charge cycle is complete.
HE mode is the default normal operating mode, and not an alarm condition. While the UPS is in this mode, the
NORMAL light on the front display will illuminate.
5.2.3
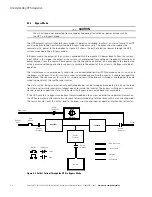
Standard Normal Mode
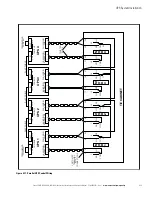
During Standard Normal mode, power for the system is derived from a utility input source through the rectifier
switchgear. Three-phase AC input power is converted to DC using IGBT devices to produce a regulated DC
voltage to the inverter. When the battery switchgear is closed the battery is charged directly from the regulated
rectifier output through a buck or boost DC converter, depending on the system voltage and the size of the
battery string attached to the unit.
Figure 5-2 shows the path of electrical power through the UPS system when the UPS is operating in Normal
mode.
The battery converter derives its input from the regulated DC output of the rectifier and provides either a
boosted or bucked regulated DC voltage charge current to the battery. The battery is always connected to the
UPS and ready to support the inverter should the utility input become unavailable.
The inverter produces a three-phase AC output to a customer's load without the use of a transformer. The
inverter derives regulated DC from the rectifier and uses IGBT devices and pulse-width modulation (PWM) to
produce a regulated and filtered AC output. The AC output of the inverter is delivered to the system output
through the inverter switchgear.
If the utility AC power is interrupted or is out of specification, the UPS automatically switches to Battery mode
to support the critical load without interruption. When utility power returns, the UPS returns to Normal mode.
Содержание 9E
Страница 1: ...Eaton 9E UPS 20 30 kVA 208 220V Generation 3 Installation and Operation Manual ...
Страница 2: ......
Страница 3: ...Eaton 9E UPS 20 30 kVA 208 220V Generation 3 Installation and Operation Manual ...
Страница 21: ...Section 1 Installation ...
Страница 22: ......
Страница 65: ...Section 2 Operation ...
Страница 66: ......
Страница 113: ......
Страница 114: ... P 164000301 1 P 164000301 1 ...