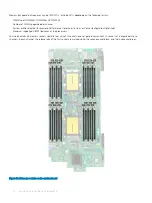
Memory Operating Mode
Description
speed, and technology, and they must be populated in sets of 6 per
processor.
Single Rank Spare Mode
Single Rank Spare Mode
allocates one rank per channel as a spare.
If excessive correctable errors occur in a rank or channel, while the
operating system is running, they are moved to the spare area to
prevent errors from causing an uncorrectable failure. Requires two
or more ranks to be populated in each channel.
Multi Rank Spare Mode
Multi Rank Spare Mode
allocates two ranks per channel as a spare.
If excessive correctable errors occur in a rank or channel, while the
operating system is running, they are moved to the spare area to
prevent errors from causing an uncorrectable failure. Requires three
or more ranks to be populated in each channel.
With single rank memory sparing enabled, the system memory
available to the operating system is reduced by one rank per
channel.
For example, in a dual-processor configuration with 24x 16 GB dual-
rank memory modules, the available system memory is: 3/4 (ranks/
channel) × 24 (memory modules) × 16 GB = 288 GB, and not 24
(memory modules) × 16 GB = 384 GB. For multi rank sparing, the
multiplier changes to 1/2 (ranks/channel).
NOTE:
To use memory sparing, this feature must be
enabled in the BIOS menu of System Setup.
NOTE:
Memory sparing does not offer protection against a
multi-bit uncorrectable error.
Dell Fault Resilient Mode
The
Dell Fault Resilient Mode
if enabled, the BIOS creates an area
of memory that is fault resilient. This mode can be used by an OS
that supports the feature to load critical applications or enables the
OS kernel to maximize system availability.
Optimizer Mode
This mode supports Single Device Data Correction (SDDC) only for memory modules that use x4 device width. It does not impose any
specific slot population requirements.
•
Dual processor: Populate the slots in round robin sequence starting with processor 1.
NOTE:
Processor 1 and processor 2 population should match.
•
Quad processor: Populate the slots in round robin sequence starting with processor 1.
NOTE:
Processor 1, processor 2, processor 3, and processor 4 population should match.
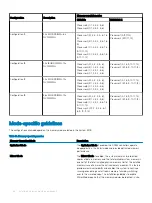
Table 12. Memory population rules
Processor
Configuration
Memory population
Memory population information
Dual processor (Start
with processor1.
processor1 and
processor 2 population
should match)
Optimized (Independent
channel) population order
A{1}, B{1},
A{2}, B{2},
A{3}, B{3},
A{4}, B{4},
Odd number of DIMM population per processor is
allowed.
Installing and removing sled components
83