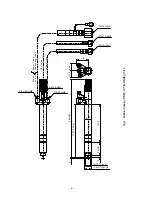
– 3 –
2.
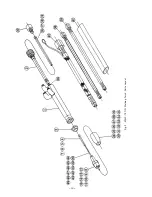
Standard Incorporated Parts
Make sure that the following are incorporated when unpacked.
Table 2 Standard Incorporated Parts
Name Part
No.
Quantity
Remarks
Collet (3.2)
H21B17
1
Insulator
H21B60
1
For gas lens
Lea collet (3.2)
H561C05
1
“O” ring (P.12)
3572-012
1
JISB2401P12
(Silicon rubber)
Nozzle (No.8)
H21B44
1
Ceriated tungsten
electrode
0870-032 1
φ
3.2
×
150mm
Note: The above are standard specifications. We have a wide selection of optional parts so that you can
do a wide range of welding by replacing the replaceable part with a respective option.
For more details, see PARTS LIST on pp.8.
3.
Functions of the Main Parts
3.1 Tungsten Electrode
Ceriated tungsten electrode (2% cerium contained,
φ
3.2
×
150mm) is incorporated for standard
specifications. See pp.8 for tungsten electrode with other diameter.
3.1.1
Selection of Electrode
Ceriated tungsten (2% cerium contained, gray mark), thoriated tungsten (2 % thorium contained, red
mark) and pure tungsten (white mark) are commonly used as tungsten electrode.
Table 3 Selection of Electrode
Welding method
(power source)
Materials of electrode
Materials of wokpiece
DC TIG welding
Ceriated tungsten (2% cerium contained)
Thoriated tungsten (2% thorium contained)
Stainless steel, mild steel, brass,
high carbon steel, cast iron,
copper, titanium, silver
AC TIG welding
Ceriated tungsten (2% cerium contained)
Pure tungsten
Thoriated tungsten (2% thorium contained)
Aluminum, aluminum casting,
magnesium, magnesium casting
Note: The table above lists only typical electrode and workpiece materials.
3.1.2
Selection of Electrode Diameter
Apply welding current within the range specified in Table 4 according to electrode diameter
Table 4 Relationship between Electrode Diameter and Welding Current
Welding current (A)
DC TIG welding (negative electrode)
AC TIG welding
Electrode
diameter
mm
φ
Ceriated
tungsten
Thoriated tungsten
Ceriated
tungsten
Pure tungsten
Thoriated
tungsten
1.0
–
1 – 80
–
10 – 60
20 – 80
1.6
5 – 150
5 – 150
40 – 130
20 – 100
40 – 130
2.4
20 – 250
20 – 250
70 – 220
50 – 160
70 – 220
3.2
50 – 400
50 – 400
110 – 290
100 – 210
110 – 290
Note: This table describes the standard ranges of welding current that differ according to electrode
diameter.