10
P/N: 192090087 REV. AA
October 2021
MAINTENANCE (CONTINUED)
OPTIONAL LOAD LIMITER
The LSB-C lever hoist has an optional load limiter, a device
that is designed and calibrated to prevent excessive overloads.
Excessive overload is indicated by lever movement without the
corresponding movement of the lower hook block or load when
the unit is operated in the “UP” direction. If overload exists,
immediately switch the lever to the “DOWN” position and operate
the lever to remove the excess load from the units.
Reducing the load to the rated capacity or less will automatically
restore the normal operation of the unit. To convert a standard
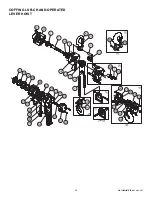
LSB-C lever hoist to a unit with the overload protection, replace
reference no. 80 (See Figure 9).
Refer to chart below for the appropriate load limiter for your
capacity hoists.
Figure 9: Overload Protection Device
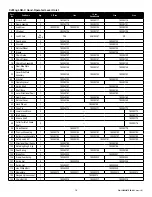
Hoist Capacity
(Tons)
Part
No.
Ket Part Number
3/4
80
IRB5080U
1
80
JRB5080U
1-1/2
80
KRB5080CU
3
80
NRB5080U
6
80
QRB5080U
Table 4: Overload Protection Kits
The load limiter may require adjustment when it slips at or below
the rated load. Refer to chart below for the correct torque setting
for the load limiter. Only adjust the load limiter by item 110 in
Figure 9. If the load limiter cannot be corrected by adjusting the
torque setting or if any of the parts are damaged, replace the
load limiter. A special tool is required to adjust Item 110 properly
(Contact factory).
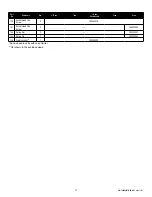
Hoist Capacity
(Tons)
Torque Range (ft-lbs)
LSB1500B
28-32
LSB3000B
59-66
LSB6000B
77-85
LSB1500B
77-85
Table 5: Torque Range
NOTE: Excessive torque will damage the load limiter and could
cause equipment damage or personal injury.
CAUTION
The load limiter is subject to overheating and wear when
excessively actuated. For this reason, once overloading is
detected, remove the excess load, restore normal operation, and
watch for any continued undue operation.
The load limiter is designed to operate dry, without lubrication. To
ensure proper operation, DO NOT apply lubricant to the friction
surfaces or to adjacent parts of the load limiter.
TESTING
Test the load limiter during periodic inspections. To perform
this test, attach the lower hook to a load at maximum 200% of
rated capacity and operate the unit in the “UP” direction. When
attempting to lift the load, the lever should slip. After this test,
move the trigger to the “DOWN” position and operate the unit to
remove the tension from the units. Once tension releases, the
unit should return to normal operation. If the load does not slip at
200% of capacity, replace the load limiter.
RECOMMENDED SPARE PARTS
Ratchet Disc Assembly
Latch Kit
Upper & Lower Hook Assembly
!
WARNING
Alterations or modifications of equipment and use of any parts
other than Coffing LSB-C lever hoist repair parts can lead to
dangerous operation and injury.
TO AVOID INJURY:
Do not alter or modify equipment. Only use replacement parts
provided by Coffing LSB-C.
PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
In addition to conducting inspections, establish a preventative
maintenance program to prolong the useful life of the hoist and
maintain its dependability and continued safe use.
The program should include periodic inspections focusing on
lubricating various components using the recommended lubricants
(See Table 7).
TESTING
Prior to initial use, the user should test all repaired or used hoists
that have not been operated for the previous 12 months, checking
for proper operation.
1.
Test the unit first in the unloaded state.
2.
Then test the unit with a light load of 100 lbs (45 kg) times the
number of load-supporting parts of load chain to be sure it
operates properly and the brake holds the load when the lever
is released.
3.
Then test the unit with a load of 125% of rated capacity.
4.
In addition, test hoists in which load-sustaining parts have
been replaced. Test them at 125% of rated capacity by or
under the direction of a designated person and prepare a
written report for record purposes.
NOTE: For additional information on inspection and testing, refer
to ASME B30.21, “Manually Operated Lever Hoists” (obtainable
from asme.org).