Diagnosis
EL3783
160
Version: 1.1
6
Diagnosis
6.1
Diagnostics – basic principles of diag messages
DiagMessages
designates a system for the transmission of messages from the EtherCAT Slave to the
EtherCAT Master/TwinCAT. The messages are stored by the device in its own CoE under 0x10F3 and can
be read by the application or the System Manager. An error message referenced via a code is output for
each event stored in the device (warning, error, status change).
Definition
The
DiagMessages
system is defined in the ETG (
) in the guideline ETG.1020,
chapter 13 “Diagnosis handling”. It is used so that pre-defined or flexible diagnostic messages can be
conveyed from the EtherCAT Slave to the Master. In accordance with the ETG, the process can therefore be
implemented supplier-independently. Support is optional. The firmware can store up to 250 DiagMessages in
its own CoE.
Each DiagMessage consists of
• Diag Code (4-byte)
• Flags (2-byte; info, warning or error)
• Text ID (2-byte; reference to explanatory text from the ESI/XML)
• Timestamp (8-byte, local slave time or 64-bit Distributed Clock time, if available)
• Dynamic parameters added by the firmware
The DiagMessages are explained in text form in the ESI/XML file belonging to the EtherCAT device: on the
basis of the Text ID contained in the DiagMessage, the corresponding plain text message can be found in
the languages contained in the ESI/XML. In the case of Beckhoff products these are usually German and
English.
Via the entry
NewMessagesAvailable
the user receives information that new messages are available.
DiagMessages can be confirmed in the device: the last/latest unconfirmed message can be confirmed by the
user.
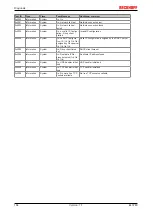
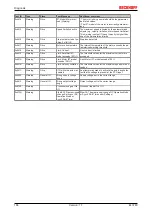
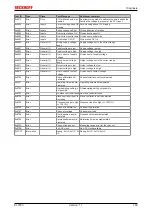
In the CoE both the control entries and the history itself can be found in the CoE object 0x10F3:
Fig. 188: DiagMessages in the CoE
The subindex of the latest
DiagMessage
can be read under x10F3:02.