UG-883
ADP1974-EVALZ User Guide
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 12
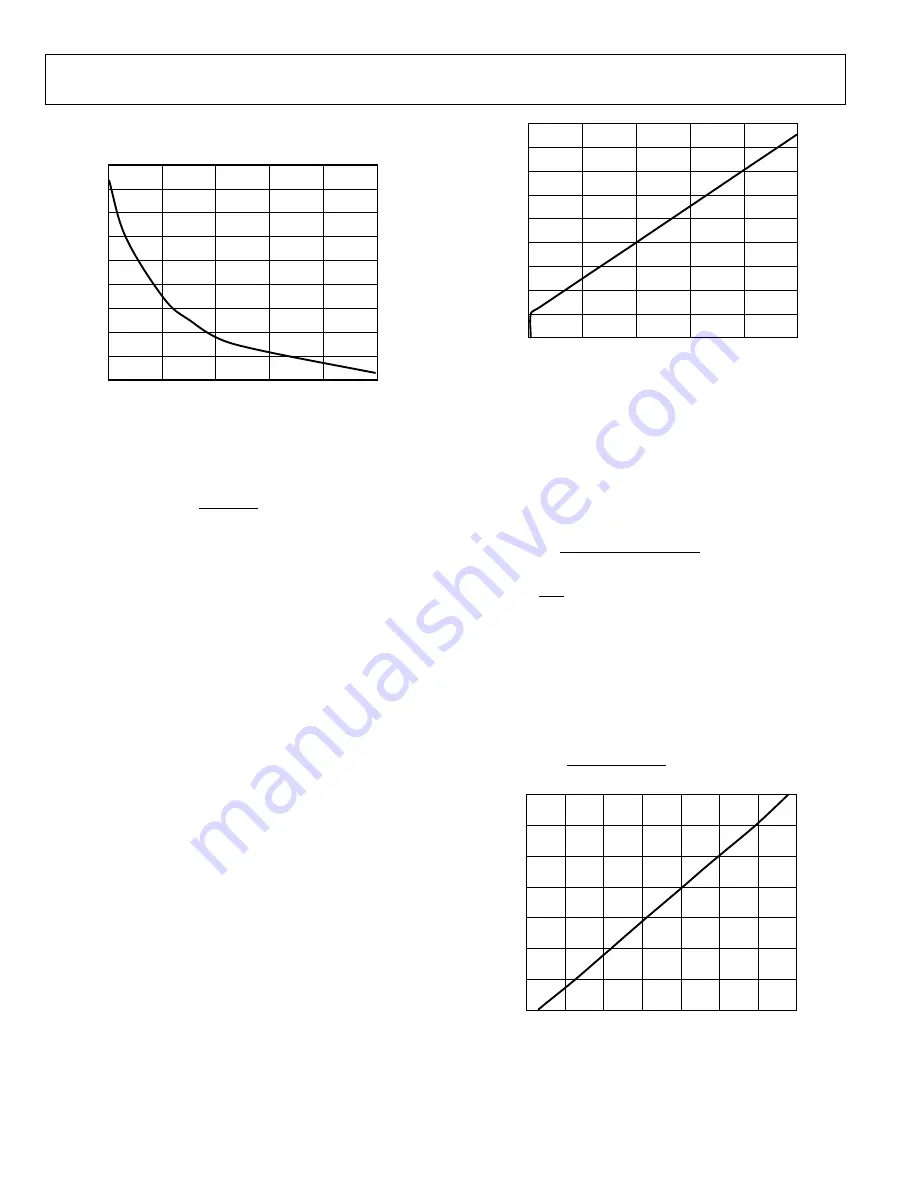
Figure 11 shows the relationship between the R
FREQ (MASTER)
value
and the programmed switching frequency.
210
30
50
70
90
110
130
150
170
190
50
100
150
200
250
300
R
F
RE
Q
(
M
AS
T
E
R)
(kΩ
)
f
SET
(kHz)
13517-
0
1
1
Figure 11. R
FREQ
(MASTER)
vs. Switching Frequency (f
SET
)
To calculate the R
FREQ
(MASTER)
value for a desired master clock
synchronization frequency, use the following equation:
( )
(kHz)
10
kΩ
4
)
(
SET
MASTER
FREQ
f
R
=
(1)
where:
R
FREQ (
MASTER
)
is the resistor in kΩ to set the frequency for master
devices.
f
SET
is the switching frequency in kHz.
Selecting R
FREQ
for a Slave Device
To configure the
ADP1974
as a slave device, drive V
SCFG
< 4.53 V.
When functioning as a slave device, the
ADP1974
operates at
the frequency of the external clock applied to the SYNC pin. To
ensure proper synchronization, select R
FREQ
to set the frequency
to a value slightly slower than that of the master clock by using
the following equation:
R
FREQ
(SLAVE)
= 1.11 ×
R
FREQ
(MASTER)
(2)
where:
R
FREQ (SLAVE)
is the resistor value that appropriately scales the
frequency for the slave device, and 1.11 is the R
FREQ
slave to
master ratio for synchronization.
R
FREQ (MASTER)
is the resistor value that corresponds to the
frequency of the master clock applied to the SYNC pin.
The frequency of the slave device is set to a frequency slightly
lower than that of the master device to allow the digital
synchronization loop of the
ADP1974
to synchronize to the
master clock period. The slave device can synchronize to a
master clock frequency running between 2% to 20% higher
than the slave clock frequency. Setting R
FREQ (SLAVE)
to 1.11× larger
than R
FREQ (MASTER)
runs the synchronization loop in approximately
the center of the adjustment range.
Phase Shift Resistor (R
SCFG
)
If a phase shift from SYNC to DH and DL is desired, select R
SCFG
for the desired time delay using Figure 12 as reference.
450
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
0
7.5
4.5
6.0
3.0
1.5
R
S
CF
G
(kΩ
)
t
DELAY
(µs)
13514-
012
Figure 12. R
SCFG
vs. Phase Delay, R
FREQ
= 100 kΩ
Programming the Dead Time (R
DT
)
To adjust the dead time on the synchronous DH and DL
outputs, connect a resistor (R
DT
) from DT to GND and bypass
with a 47 pF capacitor. Select R
DT
for a given dead time using
Figure 13 or calculate R
DT
using the following equations. To
reach a single equation for R
DT
, combine the equations for V
DT
and R
DT
.
( )
( )
(
)
3.76
28.51
ns
V
−
×
=
DEAD
DT
DT
t
I
V
(3)
DT
DT
DT
I
V
R
=
(4)
where:
V
DT
is the DT pin programming voltage.
I
DT
is 20 µA, typical internal current source.
t
DEAD
is the desired dead time in ns.
R
DT
is the resistor value in kΩ for the desired dead time.
To calculate R
DT
for a given t
DEAD
, the resulting equation used is
( )
( )
3.76
28.51
ns
kΩ
−
=
DEAD
DT
t
R
(5)
13517-
013
R
DT
(kΩ
)
t
DEAD
(ns)
0
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
Figure 13. DT Pin Resistance (R
DT
) vs. Dead Time (t
DEAD
)




























