Chapter 2. Primary CLI Syntax Reference
22
3ware 9000 Series Serial ATA Controller CLI Guide
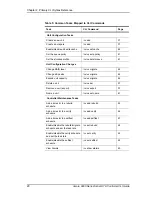
Information about commands is organized by the object on which the
commands act:
Shell Object Commands.
Shell object commands set the focus or provide
information (such as alarms, diagnostics, rebuild schedules, and so forth)
about all controllers in the system. For details, see “Shell Object Commands”
on page 23.
Controller Object Commands.
Controller object commands provide
information and perform actions related to a specific controller. For example,
you use controller object commands for such tasks as seeing alarms specific
to a controller, creating schedules during which background tasks are run, and
setting policies for the controller. You also use the controller object command
/cx add type
to create RAID arrays. For details, see “Controller Object
Commands” on page 28.
Unit Object Commands.
Unit object commands provide information and
perform actions related to a specific unit on a specific controller. For example,
you use unit object commands for such tasks as seeing the rebuild, verify, or
initialize status of a unit, starting, stopping, and resuming verifies, starting
and stopping rebuilds, and setting policies for the unit. You also use the
controller object command
cx/ux migrate
to change the configuration of a
RAID array. For details, see “Unit Object Commands” on page 53.
Port Object Commands.
Port object commands provide information and
perform actions related to a drive on a specific port. For example, you use port
object commands for such tasks as seeing the status, model, or serial number
of the drive. For details, see “Port Object Commands” on page 67.
BBU Object Commands.
BBU object commands provide information and
perform actions related to a Battery Backup Unit on a specific controller. For
details, see “BBU Object Commands” on page 72.
Help Commands.
Help commands allow you to display help information for
all commands and attributes. For details, see “Help Commands” on page 76.